Microplate Technique for Rh D Grouping: A Comprehensive Guide for Precision Blood Typing
Discover how the microplate technique enhances accuracy in Rh D blood group typing. This comprehensive guide covers step-by-step methods, troubleshooting tips, and the latest advancements in blood group testing technology.

Highlights
- Master the microplate technique for precise Rh D blood group typing, ensuring accurate results and patient safety in clinical settings.
- Explore how advancements in microplate technology are revolutionizing Rh D blood group testing, offering superior accuracy and efficiency.
- Learn step-by-step methods for accurate blood group identification using the microplate technique, a crucial tool in modern laboratory medicine.
The Rh D antigen plays a critical role in blood transfusion compatibility and hemolytic disease of the newborn. Accurate identification of the Rh D antigen is essential for ensuring patient safety and avoiding potentially life-threatening complications. The microplate technique for Rh D grouping has emerged as a precise, reliable method that enhances the accuracy and efficiency of blood typing in clinical settings.
Rh D Antigen
The Rh D antigen is one of the most significant antigens in the Rh blood group system. It is present on the surface of red blood cells in approximately 85% of the population, classifying individuals as either Rh-positive (D-positive) or Rh-negative (D-negative). The presence or absence of the Rh D antigen is determined by the expression of the RHD gene. Accurate Rh D grouping is essential for blood transfusion, organ transplantation, and managing Rh incompatibility in pregnancy.
Why the Microplate Technique? Advantages in Rh D Grouping
Precision and Accuracy: Why It Matters in Blood Typing
In blood typing, precision and accuracy are paramount. The microplate technique offers enhanced sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional methods, reducing the risk of false positives or negatives. By utilizing microplates, laboratories can process multiple samples simultaneously, leading to more consistent results and streamlined workflows.
Comparing Traditional Methods with Microplate Techniques
Traditional Rh D grouping methods, such as the tube agglutination test, have been widely used for decades. However, these methods are labor-intensive and prone to human error. The microplate technique, by contrast, automates many steps, minimizing the potential for error and increasing throughput. The ability to test multiple samples in parallel also makes the microplate technique more efficient and cost-effective.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing the Microplate Technique for Rh D Grouping
Preparing the Microplate: Materials and Equipment Needed
To perform the microplate technique for Rh D grouping, specific materials and equipment are required. These include:
- Microplates (typically 96-well plates)
- Positive and negative controls
- Micropipettes and tips
- Incubator
- Centrifuge
- Plate reader
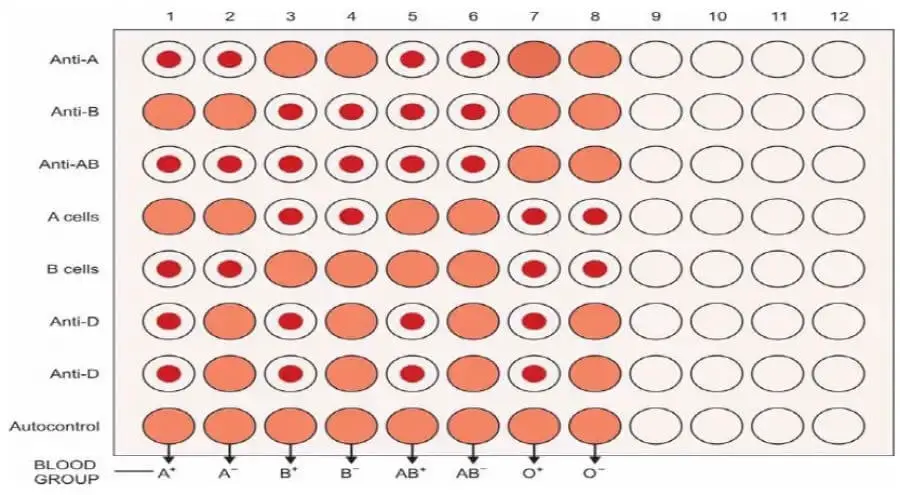
Selection of Reagents and Controls
The selection of high-quality anti-D reagents is crucial for accurate Rh D grouping. It is essential to use reagents that have been validated and are free from contaminants. Additionally, positive and negative controls should be included in each batch of tests to ensure the reliability of the results.
Calibration and Maintenance of Equipment
Proper calibration and maintenance of equipment, such as micropipettes and plate readers, are essential for ensuring the accuracy of the microplate technique. Regular calibration checks and preventive maintenance routines should be implemented to avoid discrepancies in test results.
Sample Preparation: Best Practices for Accurate Results
Proper Collection and Handling of Blood Samples
The accuracy of Rh D grouping depends significantly on the quality of the blood sample. Blood should be collected in a sterile manner, with appropriate anticoagulants used to prevent clotting. Proper labeling and handling of samples are essential to avoid cross-contamination and ensure the integrity of the results.
Ensuring Correct Dilution for Reliable Testing
Accurate dilution of blood samples and reagents is critical for obtaining reliable results. Pipettes should be used to measure precise volumes, and all dilutions should be thoroughly mixed before use. Failure to achieve the correct dilution can lead to false results, compromising patient safety.
Performing the Microplate Test: A Step-by-Step Process
Adding Reagents to the Microplate
Begin by adding the anti-D reagent to each well of the microplate according to the protocol. The reagent should be added in a consistent manner to ensure uniformity across all wells. Following the addition of the reagent, carefully add the blood sample to each well, taking care to avoid introducing air bubbles.
Incubation: Time and Temperature Considerations
Once the reagents and samples have been added to the microplate, the plate should be incubated at the recommended temperature and duration. The incubation step is critical for allowing sufficient interaction between the antigen and the reagent, leading to the formation of agglutination if the Rh D antigen is present.
Reading and Interpreting Results
After incubation, the microplate is examined for signs of agglutination. A plate reader can be used to detect and quantify agglutination, providing an objective measure of the presence or absence of the Rh D antigen. The results are then compared to the controls to confirm their validity.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in the Microplate Technique
Dealing with Weak or Unexpected Reactions
Weak or unexpected reactions can occur during the microplate technique, often due to issues such as reagent quality, sample handling, or incubation conditions. To address these issues, it may be necessary to repeat the test with fresh reagents, re-calibrate equipment, or adjust incubation parameters.
Ensuring Consistency in Reagent Quality
Inconsistent reagent quality can lead to variability in test results. Laboratories should source reagents from reputable suppliers and regularly validate their performance. Reagents should be stored according to the manufacturer's recommendations to maintain their efficacy.
Applications and Limitations of the Microplate Technique for Rh D Grouping
Clinical Applications: When to Use the Microplate Method
The microplate technique is particularly useful in settings where high-throughput testing is required, such as blood banks and large clinical laboratories. It is also valuable in cases where precise Rh D grouping is essential, such as in prenatal testing and the management of Rh-negative patients.
Recognizing the Limitations: When Another Method May Be Preferable
While the microplate technique offers numerous advantages, it may not be suitable for all situations. For example, in resource-limited settings where automation is not available, traditional methods may be more practical. Additionally, the microplate technique may not detect rare variants of the Rh D antigen, necessitating the use of more specialized tests in certain cases.
Advancements in Microplate Technology
Automation in Microplate Techniques: Improving Efficiency and Accuracy
The integration of automation in microplate techniques is a significant advancement, allowing for faster processing times and reduced human error. Automated systems can handle large volumes of samples, improve the consistency of results, and free up laboratory staff for other tasks.
Innovative Reagents and Their Impact on Blood Typing
The development of new reagents with enhanced sensitivity and specificity is another area of innovation in Rh D grouping. These reagents can improve the detection of weak D variants and other Rh antigen subtypes, further enhancing the accuracy of blood typing.
FAQs
What is a microplate?
What is a microplate reader?
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela