Determination of Blood Group by Slide Method
Learn how to quickly and accurately determine blood groups using the slide method. This guide covers essential techniques for ABO and Rh blood group testing in clinical and emergency settings.

Highlights
- Quick Blood Group Identification: The slide method offers a rapid and straightforward approach for determining ABO and Rh blood groups, essential for safe transfusions and emergency care.
- Blood Group Testing Essentials: Learn how to efficiently identify blood groups using the slide method—an essential technique in clinical settings and blood donation camps.
- Accurate Blood Group Results: Discover the best practices for conducting blood group tests using the slide method to ensure reliable and precise results every time.
The slide method for blood group determination is a widely utilized, rapid technique in clinical environments, essential for identifying an individual's ABO and Rh blood types. This method involves placing a small blood sample on a glass slide with specific anti-sera and observing the reaction for agglutination—the clumping of red blood cells. The presence or absence of this clumping reveals the blood type, which is crucial for safe transfusions, organ transplantation, and prenatal care. Although the slide method offers speed and simplicity, meticulous technique and interpretation are necessary to ensure reliable results.
Principle
In this method, red blood cells from the specimen are mixed with reagent antisera, such as anti-A and anti-B. The occurrence of agglutination indicates the presence of the corresponding antigens (agglutinogens) on the red blood cells.
Specimen
The blood sample used can be obtained from capillary blood via a finger prick or venous blood collected in EDTA anticoagulant.
Reagents
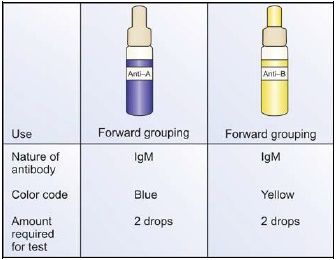
- Three types: Anti-A, anti-B, anti-A, B.
- Anti-A: Blue-colored
- Anti-B: Yellow-colored
- Anti-A, B: Colorless
- Sodium azide is added to prevent the growth of bacteria.
- Antisera are kept stored at 4-6°C to preserve their potency.
- Routinely, anti-A and anti-B are used for blood grouping
- Indications for using anti-A, B:
- for confirmation of cell grouping in newborns, and
- to resolve ABO group discrepancies
- Antisera may be polyclonal or monoclonal. Monoclonal antisera are specific, avid, and can detect weak antigens. Monoclonal antisera are commonly used minutes. Coagulation studies are carried out within 2 hours of collection of sample
Method
- Begin by preparing a clean, dry glass slide and dividing it into two sections using a glass marking pencil. Label the sections as anti-A and anti-B to correspond with the antisera being used.
- Place one drop of anti-A serum and one drop of anti-B serum in the center of the appropriate sections of the slide. Always add the antiserum first to avoid missing any reagents.
- Add one drop of the blood sample to each drop of antiserum on the slide.
- Using a separate stick or the corner of the slide, mix the antiserum and blood over an area approximately 1 inch in diameter for each section.
- Tilt the slide gently back and forth and observe the mixture for agglutination exactly two minutes after mixing.
- Results:
- Positive (+): Small clumps of red cells are visible, suspended in a clear liquid.
- Negative (–): Red cells remain evenly distributed in a uniform suspension.
- Interpret the results based on the observations, referring to standardized tables or diagrams for accuracy.
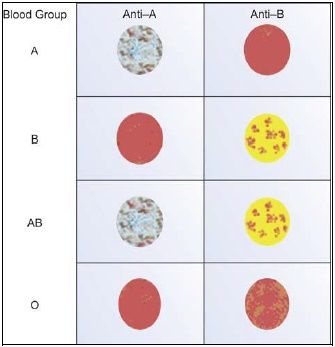
| Anti-A | Anti-B | Blood Group |
|---|---|---|
| + | - | A |
| - | + | B |
| + | + | AB |
| - | - | O |
The slide method is a quick and efficient test that requires minimal equipment, making it particularly useful in blood donation camps and emergency situations. However, it is not ideal for routine testing in blood banks due to its limitations. Weakly reactive antigens or low-titer antibodies might not be detected, and drying of the mixture at the edges could result in aggregation that mimics agglutination. Therefore, results from the slide method should always be confirmed using the more reliable tube method.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela