Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE): Principle, Procedure, and Result
Step-by-step SDS-PAGE protocol for precise protein separation and molecular weight analysis. Optimize Coomassie staining and lab workflows for accurate results.
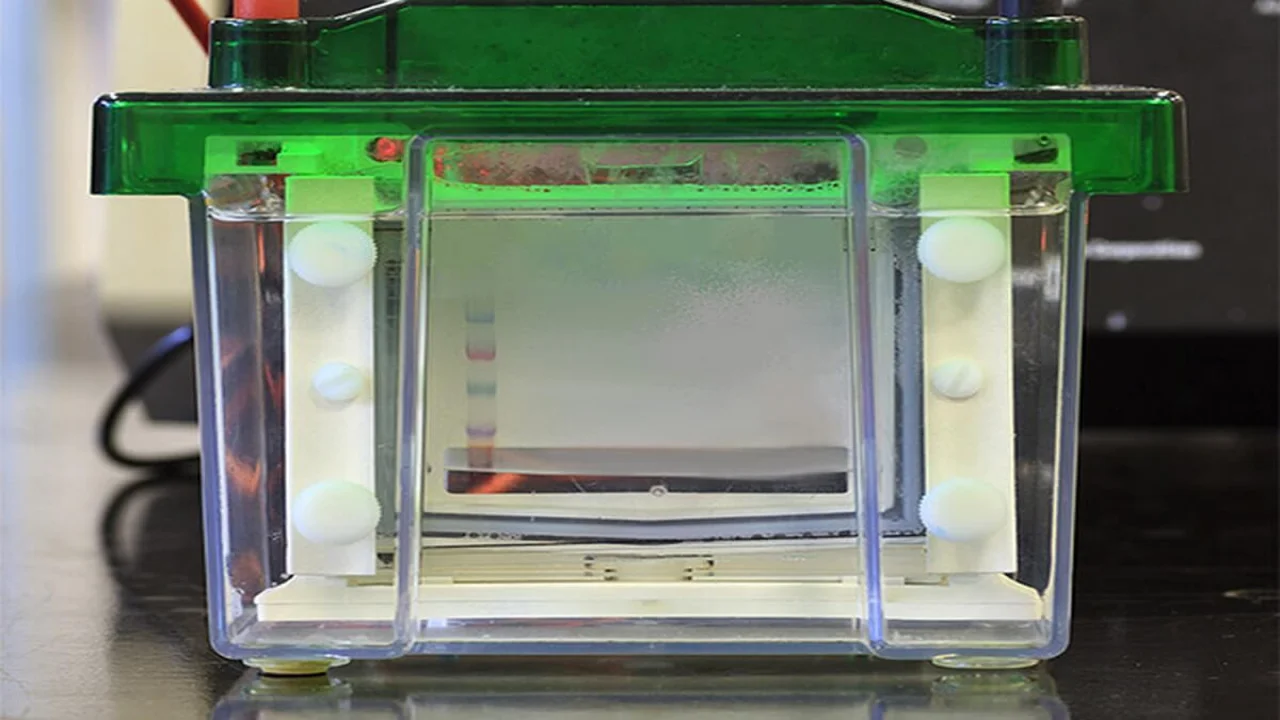
SDS-PAGE is a widely used technique to separate proteins by molecular weight under denaturing conditions. This method facilitates the analysis of protein mixtures for purity assessment, molecular weight estimation, and visualization of protein banding patterns.
Principle
SDS-PAGE employs sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), a detergent that binds to proteins, imparting a uniform negative charge proportional to their mass. This eliminates charge-based differences, ensuring separation depends solely on molecular size. Proteins migrate through a polyacrylamide gel matrix under an electric field, with smaller molecules moving faster. Key applications include:
- Evaluating protein homogeneity.
- Determining molecular weight using standardized markers.
- Visualizing protein composition in complex mixtures.
Reagents and Buffers
- Acrylamide/Bis Solution (30%):
- 29.2 g acrylamide + 0.8 g N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide dissolved in distilled water (100 mL total). Filter through Whatman No. 1 paper.
- Separating Gel Buffer (1.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8):
- Dissolve 18.17 g Tris in 60 mL water, adjust to pH 8.8 with HCl, and dilute to 100 mL.
- Stacking Gel Buffer (1 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8):
- Dissolve 6.06 g Tris in 60 mL water, adjust to pH 6.8 with HCl, and dilute to 100 mL.
- Additional Reagents:
- 10% SDS, TEMED, 10% ammonium persulfate (APS), electrophoresis buffer (25 mM Tris, 250 mM glycine, 0.1% SDS, pH 8.3).
- Sample buffer (4X): 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 2% SDS, glycerol, β-mercaptoethanol, bromophenol blue.
- Staining solution: 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) in 40% ethanol, 10% acetic acid.
- Destaining solution: 50% ethanol, 10% acetic acid.
Procedure
- Gel Preparation:
- Cleaning and Assembly: Clean glass plates with warm detergent, rinse sequentially with tap water, deionized water, and ethanol. Assemble plates with spacer strips and seal edges to prevent leakage.
- Separating Gel:
Component 8% Gel 10% Gel 15% Gel H₂O (mL) 9.3 7.9 4.6 30% Acrylamide 5.3 6.7 10.0 1.5 M Tris-HCl 5.0 5.0 5.0 10% SDS (mL) 0.2 0.2 0.2 Mix components, add 0.2 mL APS and 10–12 µL TEMED. Pour gel, overlay with water, and polymerize for 60 minutes. - Stacking Gel: Combine 6.8 mL H₂O, 1.7 mL acrylamide mix, 1.25 mL Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 0.1 mL 10% SDS, 0.1 mL APS, and 10 µL TEMED. Pour over polymerized separating gel, insert comb, and allow to set.
- Sample Preparation:
- Mix protein samples with 1X sample buffer (final concentration). Boil for 2 minutes to denature proteins.
- Electrophoresis:
- Load samples into wells. Run at 100 V (constant voltage) for 4–6 hours until bromophenol blue reaches the gel bottom.
- Staining and Destaining:
- Fix gel in 10% trichloroacetic acid (5 minutes), stain overnight with CBB, then destain until clear bands appear.
Results
SDS-PAGE resolves proteins into distinct bands corresponding to their molecular weights. By comparing bands to a protein ladder, molecular weights are estimated in kilodaltons (kDa). Homogeneous samples display a single band, while mixtures show multiple bands.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela