Flagellum in Protozoa
The classification of protozoa is based on locomotory organs. In Mastigophora protozoans, the flagellum is the locomotory organ. It is long and thread-like. It is helpful for locomotion.
The classification of protozoa is based on locomotory organs. In Mastigophora protozoans, the flagellum is the locomotory organ. It is long and thread-like. It is helpful for locomotion.
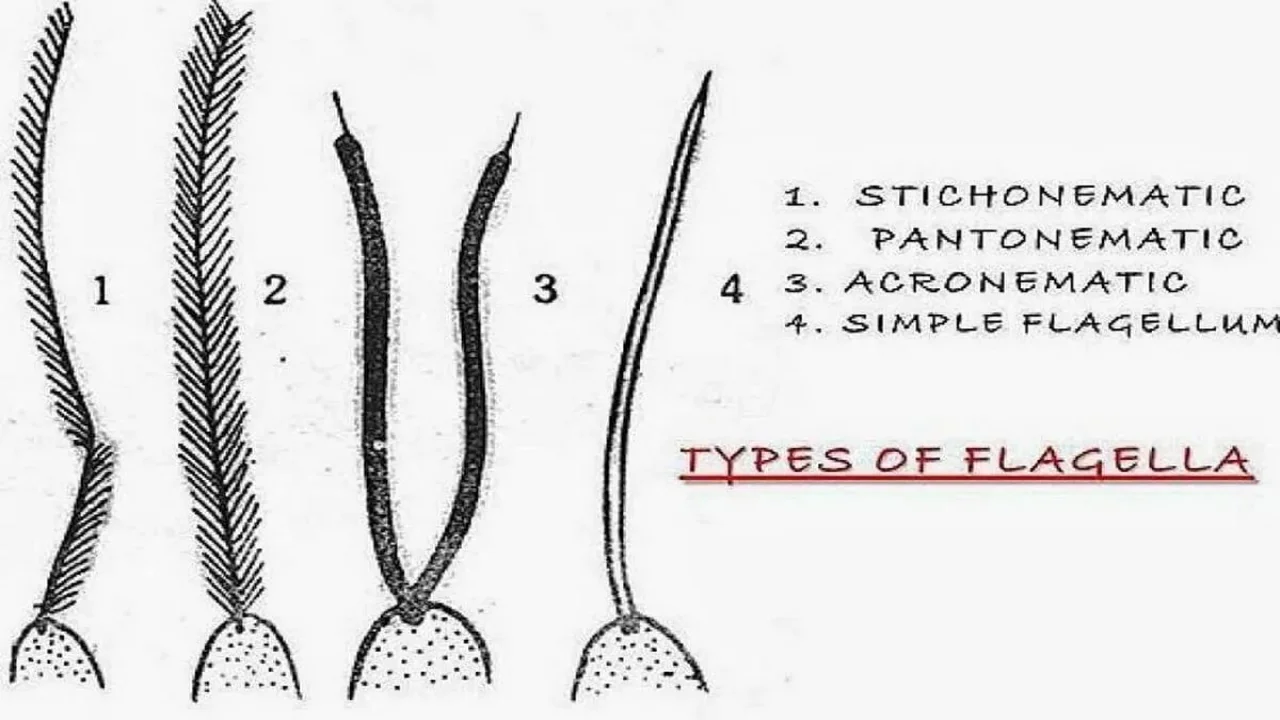
Flagella are divided into four types by the arrangement of mastigonemes on the flagellum.
- Stichonematic: Mastigonemes are in one row. E.g: Euglena
- Pantonematic: Mastigonemes are in two rows.
- Acronematic: Flagellum has no mastigonemes, it ends with a fine filament. E.g: Chlatnydomonas.
- Simple flagellum: This flagellum will not show mastigonemes or end in fiber. E.g: Dinoflagellates.
In Mastigophora organisms, one or two or many flagella are seen. If a flagellum drags the organisms it is called Tracteilum. The flagellum which pushes the organisms forward is called Pulsellum.
T.S. Of Flagellum
The flagellum T.S. shows central fibers. Around them nine pairs of peripheral fibers are present. A cytoplasmic sheath covers these fibers. Each flagellum arises 'from a basal granule. The basal granule is also called Blepharoplasty. In some cases, the blepharoplasty is connected with a nucleus, by rhinoplasty.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Comment
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela