CAUSES OF ERRONEOUS RESULTS (INTERFERENCES CAUSING ABNORMAL RESULT) WITH HEMOTOLOGY ANALYZER
Saturday, 29 July 2017 14:18CAUSES OF ERRONEOUS RESULTS (INTERFERENCES CAUSING ABNORMAL RESULT)
These are listed in Table 809.1
Table 809.1 Causes of erroneous results with hematology analyzer
| Parameter | Interfering factors |
| Erroneous increase | Erroneous decrease | |
|
0. All parameters
|
—
|
|
|
1. WBC count
|
|
|
|
2. RBC count
|
|
|
|
3. Hemoglobin
|
|
|
|
4. MCV
|
|
|
|
5. MCHC
|
|
|
|
6. Platelets
|
|
|
| *: WBCs are counted along with RBCs, but normally their number is statistically insignificant |
FLAGGING
‘Flags’ are signals that occur when an abnormal result is detected by the analyzer. Flags are displayed to reduce false-positive and false-negative results by mandating a review of blood smear examination.

PARAMETERS MEASURED BY HEMATOLOGY ANALYZERS
Saturday, 29 July 2017 12:54
FLOW CYTOMETRY
Saturday, 29 July 2017 10:37
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN FLOWCYTOMETRY
Saturday, 29 July 2017 10:09
COMMON APPLICATIONS OF FLOW CYTOMETRY IN HEMATOLOGY
Friday, 28 July 2017 12:59
Platelet Aggregation Studies
Friday, 28 July 2017 05:05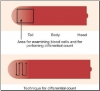
EXAMINATION OF BLOOD SMEAR
Thursday, 27 July 2017 06:22
MORPHOLOGY OF PLATELETS
Wednesday, 26 July 2017 12:45
NUMERICAL ABNORMALITIES OF LEUKOCYTES
Wednesday, 26 July 2017 11:28
WHITE BLOOD CELLS MORPHOLOGY
Wednesday, 26 July 2017 08:33
RED CELLS MORPHOLOGY
Tuesday, 25 July 2017 13:19
PARTS AND FUNCTIONS OF A COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
Tuesday, 25 July 2017 10:42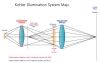
KOHLER ILLUMINATION
Tuesday, 25 July 2017 08:43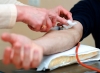
PROCEDURES FOR THE COLLECTION OF BLOOD FOR HEMOTOLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Monday, 24 July 2017 05:21
Setting the record straight: Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) do not cause dementia
Sunday, 23 July 2017 07:00
SEQUENCE OF FILLING OF TUBES FOR HEMOTOLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Saturday, 22 July 2017 07:14
