Mealworm: Characteristics, Lifecycle, Farm Setup, and Nutrient Benefits
Explore a comprehensive guide on mealworms, covering their characteristics, life cycle, and how to set up your own mealworm farm. Learn about harvesting mealworms and their role as a nutrient source for chickens, reptiles, birds, and small mammals.

Mealworms, scientifically known as Tenebrio molitor, are not only intriguing creatures but also serve as vital components in the natural world. Mealworms are the larval form of darkling beetles and are commonly found in environments with decaying organic matter. Their adaptability and resilience make them essential decomposers, breaking down dead plant material and recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process is crucial for maintaining the balance of nutrients in ecosystems and promoting healthy soil quality.
In addition to their role as decomposers, mealworms also serve as a valuable food source for a wide range of animals, including birds, reptiles, and small mammals. Their high protein content and nutritional value make them a popular choice for feeding pets and livestock. This aspect highlights the interconnectedness of different species in the food chain and underscores the importance of mealworms in supporting biodiversity.
Mealworms have gained popularity in recent years as a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative protein source for human consumption. As the global demand for protein continues to rise, mealworms offer a promising solution that requires fewer resources and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional livestock farming. This aspect of mealworms' versatility underscores their potential to address food security challenges and promote sustainable practices in agriculture.
Beyond their ecological and nutritional significance, mealworms also hold cultural and economic importance in various societies around the world. In some cultures, mealworms are considered a delicacy and are incorporated into traditional dishes as a source of protein and flavor. Additionally, the commercial production of mealworms for pet food, livestock feed, and human consumption has created new opportunities for entrepreneurship and innovation in the agricultural sector.
Characteristics of Mealworms
Mealworms are the larval form of darkling beetles, belonging to the Tenebrionidae family. These creatures are typically cylindrical in shape, with a segmented body consisting of a head, thorax, and abdomen. They have a hard exoskeleton that provides protection and support as they navigate through their environment. Mealworms are known for their distinct appearance, with a creamy white color and a slightly curved body.
One of the most remarkable characteristics of mealworms is their adaptability and resilience. These creatures can thrive in a wide range of environmental conditions, making them well-suited for various habitats. Their ability to break down dead plant material and recycle nutrients back into the soil is essential for nutrient cycling in ecosystems. This process not only helps maintain soil quality but also supports the growth of plants and other organisms in the ecosystem.
Taxonomy of Mealworm Beetles (Tenebrio molitor)
The scientific name for mealworms is Tenebrio molitor, which falls under the kingdom Animalia, phylum Arthropoda, class Insecta, and order Coleoptera. Within the Tenebrionidae family, Tenebrio molitor is a well-known species that has been extensively studied due to its ecological significance and economic value.
Mealworm beetles, the adult form of mealworms, undergo a complete metamorphosis from larvae to pupae and finally to adults. This transformation is a fascinating process that highlights the complexity and diversity of insect life cycles.
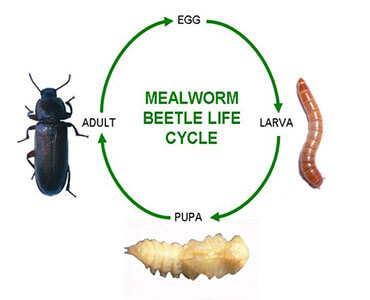
The Mealworm Life Cycle
In line with the developmental trajectory observed in holometabolic insects, they traverse a sequence of four distinct life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Larvae, characterized by their elongated bodies, typically exhibit dimensions of approximately 2.5 centimeters or more, whereas adults manifest dimensions ranging between 1.25 and 1.8 centimeters in length.
- Egg Stage: The mealworm life cycle begins with the egg stage, where adult female beetles lay tiny, oval-shaped eggs. These eggs are typically white or cream-colored and are deposited in dark, sheltered areas within the mealworm habitat. Under optimal conditions of warmth and humidity, the eggs hatch within 4-19 days, giving rise to tiny mealworm larvae.
- Larval Stage: Once hatched, the mealworm larvae enter the larval stage, characterized by rapid growth and development. During this phase, the larvae feed voraciously on organic matter, such as grains, vegetables, and fruits, to fuel their growth. As they consume nutrients and grow in size, the larvae shed their exoskeletons multiple times in a process known as molting. Each molt allows the larvae to increase in size and reach the next developmental stage.
- Pupal Stage: After undergoing several molts and reaching a mature size, the mealworm larvae enter the pupal stage, where they undergo a remarkable process of metamorphosis. During this stage, the larvae transform into pupae, undergoing internal changes that prepare them for their final transition into adult beetles. The pupal stage is a critical period of development where the internal structures and organs of the mealworm undergo significant restructuring to support the emergence of the adult beetle.
- Adult Stage: Following the completion of metamorphosis, the pupae emerge as adult mealworm beetles, marking the final stage of the mealworm life cycle. Adult beetles are typically dark brown or black in color, with hardened exoskeletons and distinctive body segments. Once emerged, adult beetles are ready to mate and reproduce, continuing the cycle of life by laying eggs and initiating a new generation of mealworms.
Setting Up Your Mealworm Farm
Setting up your mealworm farm involves creating a conducive environment for the optimal growth and development of your mealworm colony. By carefully selecting the right environment, choosing appropriate containers, and providing suitable substrate, you can ensure the well-being of your mealworms and maximize their productivity.
Selecting the Right Environment
The first step in setting up your mealworm farm is to choose the right environment for your colony. Mealworms thrive in a warm and dark setting, making a well-ventilated room with a consistent temperature between 75-80°F ideal for their growth. Avoid placing your mealworm farm in direct sunlight or areas with extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can stress the colony. Additionally, ensure that the environment is free from pests and other potential contaminants that could harm your mealworms.
Choosing the Appropriate Containers
When it comes to housing your mealworms, selecting the right containers is crucial for their well-being. Opt for containers that are well-ventilated to prevent moisture buildup and allow for proper airflow. Plastic storage bins or containers with lids that have small ventilation holes are popular choices for mealworm farms. Make sure the containers are spacious enough to accommodate the growing colony and provide ample room for movement. It's also essential to regularly clean and sanitize the containers to maintain a hygienic environment for your mealworms.
Providing Suitable Substrate
Choose a suitable substrate that not only serves as a bedding material but also provides essential nutrients for your colony. Common substrates for mealworm farms include wheat bran, oats, or a mixture of grain and vegetable matter. The substrate should be dry, clean, and free from contaminants to ensure the health of your mealworms. Additionally, consider adding pieces of fruits or vegetables as supplemental food sources for your colony to enhance their nutritional intake.
Feeding and Nutrition
Mealworms are omnivorous creatures that consume a variety of organic materials. They primarily feed on grains, vegetables, fruits, and other plant matter. In a controlled farm environment, you can provide mealworms with a balanced diet that mimics their natural food sources. This can include wheat bran, oats, carrots, apples, and other nutritious foods. It's essential to offer a diverse diet to ensure that your mealworms receive all the necessary nutrients for their growth and development.
Optimal diets for mealworms should be rich in protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals. Protein is particularly important for the growth and reproduction of mealworms, making it a crucial component of their diet. Foods like oats, wheat bran, and dried insects are excellent sources of protein for mealworms. Fiber is essential for their digestion and overall gut health, so including fibrous foods like carrots and apples in their diet is beneficial. Additionally, providing a variety of fruits and vegetables can ensure that your mealworms receive a wide range of vitamins and minerals essential for their well-being.
When it comes to the nutritional value of mealworms for chickens, these insects are a highly beneficial and nutritious food source. Mealworms are rich in protein, making them an excellent supplement to a chicken's diet, especially for growing chicks and laying hens. The protein content in mealworms helps support muscle development, feather growth, and overall health in chickens. Additionally, mealworms are a good source of essential amino acids, which are vital for various physiological functions in chickens.
Incorporating mealworms into a chicken's diet can also enhance their egg production and quality. The nutrients present in mealworms can contribute to stronger eggshells, improved yolk color, and overall egg nutrition. By feeding chickens mealworms, you can provide them with a natural and nutritious source of protein and essential nutrients that can positively impact their health and productivity.
Maintaining Your Mealworm Colony
Maintaining a healthy and thriving mealworm colony requires attention to various factors, including temperature and humidity control, regular cleaning and maintenance, and troubleshooting common issues that may arise. By following proper care practices, you can ensure the well-being of your mealworms and optimize their growth and productivity.
Temperature and Humidity Requirements
One of the key factors in maintaining a successful mealworm colony is providing the right temperature and humidity levels. Mealworms thrive in a warm and dry environment, with temperatures ideally ranging between 75-80°F (24-27°C). It's essential to avoid extreme temperature fluctuations, as this can stress the mealworms and impact their growth and reproduction rates.
Humidity levels are equally important for the health of your mealworm colony. Mealworms require a relatively dry environment, with humidity levels around 70%. Excessive moisture can lead to mold growth and bacterial contamination, which can be harmful to the mealworms. To maintain optimal humidity levels, ensure proper ventilation in the mealworm containers and avoid over-misting the bedding material.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential tasks to keep your mealworm colony healthy and productive. Here are some tips to help you maintain a clean and hygienic environment for your mealworms:
- Remove uneaten food: Regularly check the mealworm containers and remove any uneaten food to prevent mold growth and bacterial contamination.
- Replace bedding material: Over time, the bedding material in the mealworm containers may become soiled and contaminated. Replace the bedding material regularly to maintain a clean and odor-free environment for the mealworms.
- Clean containers: Periodically clean the mealworm containers with a mild soap solution to remove any debris or residue. Rinse thoroughly and allow the containers to dry completely before reintroducing the mealworms.
- Monitor for pests: Keep an eye out for any signs of pests, such as mites or beetles, in your mealworm containers. If you notice any pests, take immediate action to prevent infestations and protect your mealworm colony.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite your best efforts, you may encounter some common issues when maintaining your mealworm colony. Here are some troubleshooting tips for addressing these issues:
- Mold growth: If you notice mold growing in the mealworm containers, reduce the humidity levels by increasing ventilation and avoiding over-misting. Remove any moldy food and bedding material promptly to prevent further contamination.
- Escapees: Mealworms are known to be escape artists, so make sure your containers have secure lids to prevent them from crawling out. Check the containers regularly for any gaps or openings that may allow mealworms to escape.
- Slow growth or reproduction: If you observe slow growth or reproduction rates in your mealworm colony, review your feeding and maintenance practices. Ensure that the mealworms are receiving a balanced diet, optimal temperature, and proper care to support their growth and reproduction.
By maintaining the right temperature and humidity levels, implementing proper cleaning and maintenance routines, and addressing common issues promptly, you can ensure the health and productivity of your mealworm colony. Following these guidelines will help you create an optimal environment for your mealworms to thrive and contribute to the success of your mealworm farming venture.
Harvesting Mealworms
Harvesting mealworms involves knowing when they are ready for harvest, employing effective techniques to gather them, and ensuring proper storage for future use.
Knowing When Mealworms Are Ready for Harvest
Mature mealworms are typically ready for harvest when they reach their final larval stage, known as the pupa stage. At this point, they are plump, firm, and have a creamy white color. Avoid harvesting mealworms that are still in the larval stage, as they may not have reached their full size and nutritional value.
Techniques for Harvesting Live Mealworms
There are several techniques you can use to gather them efficiently and minimize stress on the insects. One common method is to sift the mealworms from their bedding using a fine mesh sieve or a specialized mealworm scoop. Gently shake the container to encourage the mealworms to move towards the surface, making it easier to separate them from the substrate.
Another technique involves using a carrot or potato slice as bait to lure the mealworms out of their bedding. Simply place the vegetable slice on top of the substrate and wait for the mealworms to crawl onto it. Once they have gathered on the bait, carefully transfer them to a separate container for further processing or storage.
Storing Harvested Mealworms
After harvesting your mealworms, proper storage is essential to maintain their quality and prolong their shelf life. One effective way to store harvested mealworms is by refrigerating them. Place the mealworms in a breathable container, such as a ventilated plastic tub or a mesh bag, and store them in the refrigerator at a temperature between 40-50°F (4-10°C). This will help slow down their metabolism and extend their lifespan.
Alternatively, you can freeze the harvested mealworms for long-term storage. Spread them out in a single layer on a baking sheet and place them in the freezer until they are frozen solid. Once frozen, transfer the mealworms to a resealable plastic bag or airtight container and store them in the freezer. Frozen mealworms can be kept for several months and used as needed for feeding pets, wild birds, or for other purposes.
Utilizing Mealworms
After successfully harvesting your mealworms, you may be wondering about the various ways you can utilize these nutritious insects. Mealworms are not only a sustainable protein source but also have versatile applications in animal feed, pet nutrition, and even human consumption.
Mealworms as Sustainable Protein Sources
One of the key benefits of mealworms is their high protein content, making them an excellent alternative protein source. They are rich in essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious option for supplementing animal diets. Whether you are raising poultry, fish, reptiles, or even wild birds, mealworms can serve as a valuable protein source to support their growth and overall health.
In addition to their nutritional value, mealworms are also environmentally friendly. They require significantly less water, land, and feed compared to traditional livestock, making them a sustainable protein source with a lower ecological footprint. By incorporating mealworms into animal feed, you can contribute to more sustainable and efficient food production practices.
Applications in Animal Feed and Pet Nutrition
Mealworms are commonly used in animal feed formulations due to their high protein content and digestibility. They can be fed to a wide range of animals, including chickens, ducks, geese, fish, and even exotic pets like reptiles and amphibians. Mealworms can be offered live, dried, or in powdered form, providing flexibility in how they are incorporated into different diets.
For pet owners, mealworms are a popular choice for enhancing the nutritional value of their pets' diets. Many reptiles, birds, and small mammals benefit from the protein and essential nutrients found in mealworms. Whether you have a bearded dragon, a parrot, or a hedgehog, adding mealworms to their diet can help meet their dietary requirements and promote overall well-being.
Potential Benefits for Human Consumption
While the idea of consuming insects may be unconventional in some cultures, mealworms offer a promising source of sustainable protein for human consumption. They are rich in protein, healthy fats, and micronutrients, making them a nutritious addition to the human diet. Mealworms can be incorporated into various dishes, such as protein bars, pasta, burgers, and even baked goods, providing a sustainable protein source for health-conscious consumers.
Insects like mealworms are also being explored as a solution to global food security challenges. With a growing world population and increasing demand for protein, edible insects offer a sustainable and efficient way to meet dietary needs without putting excessive strain on the environment. By considering mealworms as a viable food source, we can move towards more sustainable food production systems and reduce our reliance on traditional livestock.
In conclusion, mealworms are not just a valuable resource for animal feed and pet nutrition but also hold great potential for human consumption. By recognizing the nutritional benefits and sustainability of mealworms, we can explore innovative ways to incorporate these versatile insects into our diets and contribute to a more sustainable food future.
FAQs
What do mealworms turn into?
What are the common misconceptions about mealworms?
Addressing concerns about mealworm farming.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Comment
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela