Search
Total 52 results were found for your query zoology.
-
 Zoology
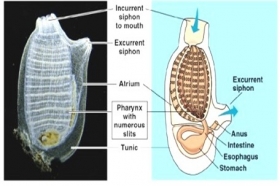
ZoologyGENERAL CHARACTERS OF UROCHORDATA
The tunicates were first regarded as sponges. Lamark in 1816 placed Tunicata in between the Radiata and Vermes in his system of classification. Later, they were included in Mollusca. In 1866 Kowalevsky ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
 Zoology
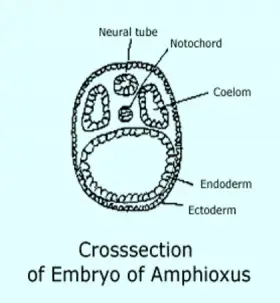
ZoologyORGANOGENY IN AMPHIOXUS
The development of organ system is called as Organogeny. In Amphioxus the gastrula elongates in the future anteroposterior direction and the blastopore comes nearer to the posterior end of the dorsal surface ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
 Zoology
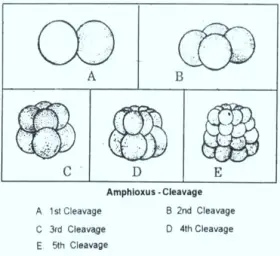
ZoologyREPRODUCTION IN AMPHIOXUS: POST FERTILISATION CHANGES
FATEMAP OF FERTILISED EGG OF AMPHIOXUS: Conklin in 1932 studied the fate map of Amphioxus. In 1962 Tunguntung described the egg of amphioxus 4 regions are clearly seen. Clear cytoplasm occupying ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
 Zoology
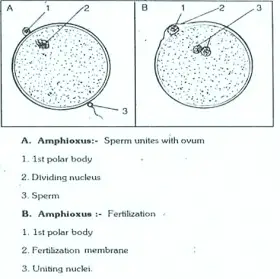
ZoologyREPRODUCTION IN AMPHIOXUS
Amphioxus is a Cephalochordate animal. Its Life history in the early stages shows resemblance with ascidians. HATSCHE’K WILSON. CONKLIN’ worked on the part of embryogenesis of Amphioxus. ‘CONKLINS’ work ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
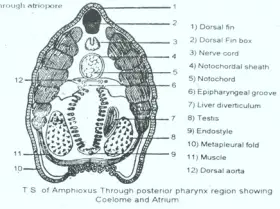 Zoology
ZoologyATRIUM IN AMPHIOXUS
In amphioxus a big space is present, called Atrium it is lined by ectoderm. It encloses pharynx, and part of intestine. It opens out through atriopore at 36 myotome in front of caudal fin. The dorsal wall ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
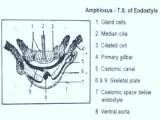 Zoology
ZoologyENDOSTYLE IN AMPHIOXUS
In the Urochordate and Cephalochordate animals the ventral side of the pharyhx wilI contains endostyle. It is a glandular ciliated groove present on the floor of the pharynx. This contains alternate bands ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
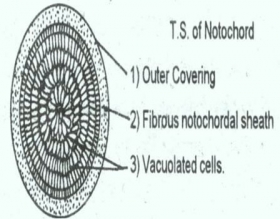 Zoology
ZoologyNOTOCHORD IN AMPHIOXUS
In chordate animals notochord, dorsal tubular nerve cord and pharyngeal slits are present. In Amphioxus notochord is a cylindrical rod extending the whole length of the body from anterior end to ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologySKELETON IN AMPHIOXUS
Exoskeleton is absent in Branchiostama. Endoskeleton include the notochord, gelatinous rods and plates, fin-ray boxes etc. 1. Notochord in Amphioxus: The notochord of Amphioxus is extending the whole ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
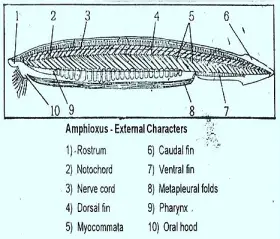
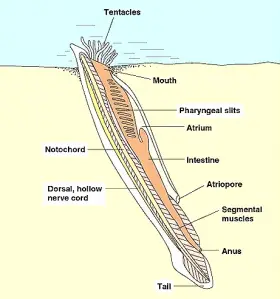 Zoology
ZoologyEXTERNAL CHARACTERS OF AMPHIOXUS
Amphioxus belongs to Cephalochordate. In 1778 Amphioxus was first discovered and described by Palias. He called it a Molluscan animal. In 1834, it was described as a chordate animal by Costa. He called ...Created on 05 July 2017 -
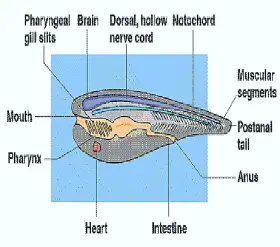 Zoology
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION AND SYSTEMIC POSITION OF CEPHALOCHORDATE
The sub-phylum Cephalochordata includes a single class Leptocardii, which has single family, Branchiostomidae. The family contains only two genera Branchiostoma and Asymmetron. The subphylum - Cephalochordata ...Created on 05 July 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyGENERAL CHARACTERS OF CEPHALOCHORDATA
Cephalochordata includes two genera, 1. Asymmetron and 2. Branchiostoma (Amphioxus). Cephalochordates are small fish like animals which show Chordate characters. The notochord extends the entire length ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
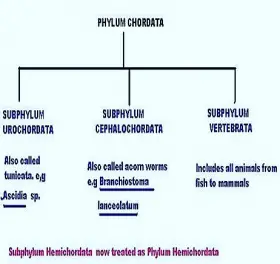 Zoology
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION PHYLUM CHORDATE
Phylum Chordate is divided into three Sub-Phyla. SUB-PHYLUM: UROCHORDATA SUB-PHYLUM: CEPHALOCHORDATA SUB-PHYLUM: VERTEBRATA The first two sub phyla are called lower chordates or PROTOCHORDATES. ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
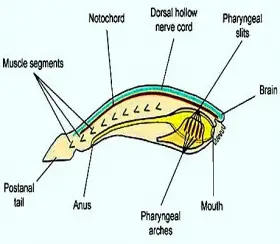 Zoology
ZoologyBIOLOGY OF CHORDATES
CHORDATES The Phylum Chordate includes bilaterally symmetrical, metamerically segmented, triploblastic, enterocoelomate metazoans exhibiting hights complex organization. This phylum is supposed to ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
 Zoology
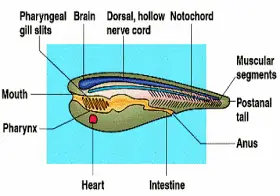
ZoologyGENERAL CHARACTERS OF CHORDATES
The animal kingdom is divided into two sub-kingdoms: Chordata Non-Chordata GENERAL CHARACTRS OF CHORDATES The Chordate characters appear in the developmental stage will persist ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
 Zoology
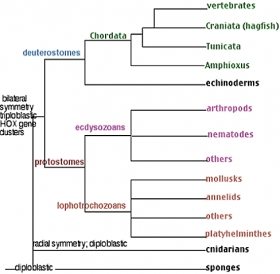
ZoologyORIGIN OF CHORDATES
THEORIES ABOUT ORIGIN OF CHORDATES It is believed that Chordates have originated from invertebrates. It is difficult to determine from which invertebrate group the chordates were developed. Chordate ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
 Zoology
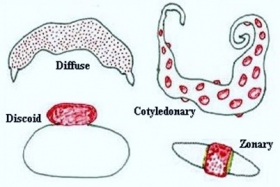
ZoologyPLACENTA IN MAMMALS: STRUCTURE, TYPES AND FUNCTIONS
In Eutherian mammals the embryo develops in the uterus of mother. The developing embryo will get nourishment from mother through the placenta. Placenta is not common to all mammals. It is developed well ...Created on 03 July 2017 -
 Zoology
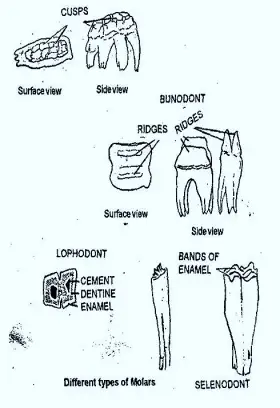
ZoologyTeeth Modifications in Mammals
There is an interrelation between the form of teeth arid nature of food. These may be omnivorous, carnivorous, insectivorous herbivorous and rodents or gnawing. In Mammals dentition is complete in the ...Created on 03 July 2017 -
 Zoology
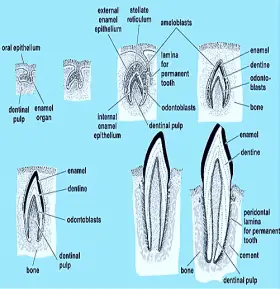
ZoologyTOOTH DEVELOPMENT IN MAMMALS
The tooth develops partly from the epidermis and partly from the mesenchyme of dermis. Its enamel is derived from the epidermis and the remaining parts from the mesenchyme. Mammalian teeth develop in two ...Created on 02 July 2017 -
 Zoology
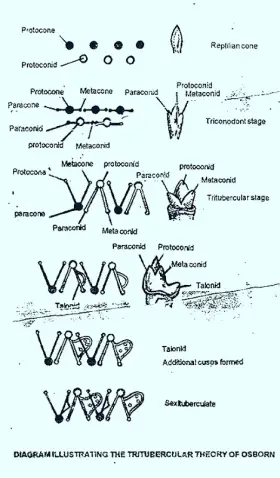
ZoologyEVOLUTION OF MAMMALIAN MOLAR
Two main theories have been proposed to explain the evolution of molars. CONCRESCENCE THEORY OF ROSE TRLTUBERCULAR THEORY OF COPE & OSBORN According to the concrescence theory, the molar ...Created on 02 July 2017 -
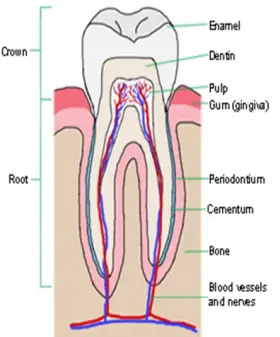 Zoology
ZoologyDENTITION IN MAMMALS
Teeth are the dermal derivatives of integument They are developed as a result of calcification in the mucous membrane of the 1 cavity. Along with the ridge of the two jaws, the teeth are arranged in a ...Created on 02 July 2017