Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Zoology
PLACENTA IN MAMMALS: STRUCTURE, TYPES AND FUNCTIONS
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Monday, 03 July 2017 12:19 UTC
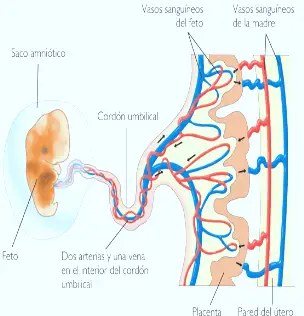
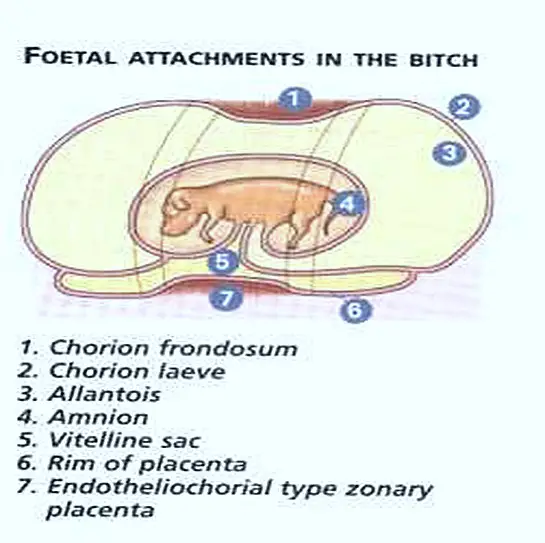
In Eutherian mammals the embryo develops in the uterus of mother. The developing embryo will get nourishment from mother through the placenta. Placenta is not common to all mammals. It is developed well in Eutheria The term placenta was delved from Greek word it means flat cake. Placenta is a special connective tissue, which contains the uterus of mother and foetal membranes of foetus.
Prototherian mammals are egg laying mammals. Hence placenta is not formed in uterus.
In marsupials the embryo develops incompletely in the uterus. They show yolk sac placenta and primitive allantoic placenta: Yolk sac placenta:
Ex: Diadelphis.
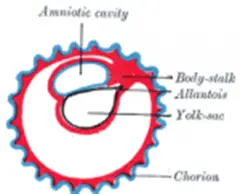
In these animals the developing embryo shows small allantois. It will never come in contact with chorion. Their yolk sac was large. It comes in contact with chorin. This part will gain blood vessels. This part will come in contact with endometrium of uterus. This is only a contact, but not fusion. Through this contact the embryo will absorb nourishment from mother. This is called chorio vitelline placenta or Yolk sac placenta.
Primitve Allantoic Placenta:
In paramoles simple allantoic placenta is developed Allantoic will enlarge It comes In contact with chonon This structure will be closely applied to mother’s uterus. It is called chorio-allantoic placenta. In these animals yolk sac placenta is not seen.
Placenta In Eutherla:
In Eutherian mammals true allantoic placenta is seen. Allantoic becomes big and comes in contact with chorion. This part will show close association with uterine wall. This connection is called placental connection. The structure of placenta will vary in different orders of Eutheria.
Placenta is classified in three ways.
- The placenta classification on nature of contact.
- Placenta is classified basis on the distribution of villi.
- Classification of placenta basing on histology.
NATURE OF CONTACT:
It is two types, Indeciduate and deciduate type.
Indeciduate type placenta: Ex: Ungulate, Cetaceans, Sirenians. Lemurs:
The chorianic villi are simple projections, they lie in contact with uterus. They have a loose contact. There is no fusion. At the time of birth of embryo uterus is not damaged.
Deciduate type Placenta: Ex: Primates, Rodentia, Insectivora, chiroptera The allantochorianic villi penetrate into uterine valli. They are intimately fused. Hence at the time of birth, the uterus is damaged. Bleeding occurs, the utrine wall enters into formation of placenta is called deciduas.
BASING ON DISTRIBUTION OF VILLI:
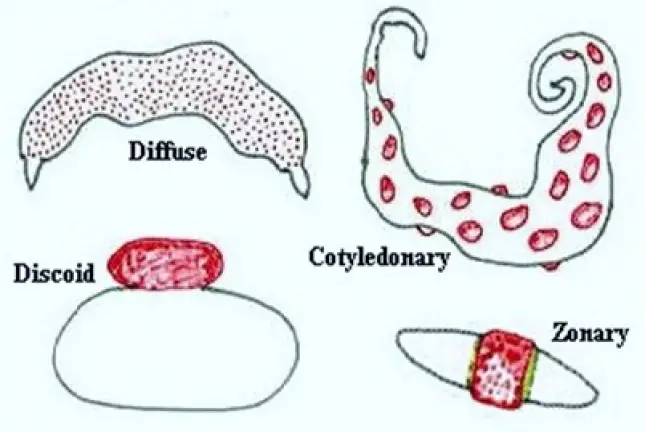
According to the distribution of villi five kinds of placenta are seen.
- Diffused type placenta: Ex: Horse, pig. The villi are uniformly distributed on the surface of blastocyst, except at the extreme ends.
- Cotyledonary placenta: Ex: Sheep, Cow, Deer. The villi are arranged in groups. Each group is called cotyledon. Each cotyledon fits into caruncla fo uterus.
- Intermediate type Placenta: Ex: Cainel, Giraffe. It is a rare type, it shows free villi on cotyledons. Hence it is called intermediate type placenta.
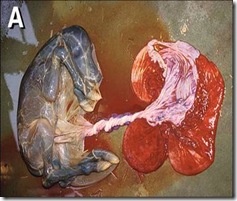
In these three types of placenta during perturition the foetus will not damage uterus. - Zonary placenta: Ex: Cat, Dog, Carnivores. The villi are In the form of transverse zones. In dog a single girdle of vhf will be present. In fox two girdles of villi are present. The villi penetrate Into uterine wall. Hence during parturitlon uterine wall Is damaged.
- Discoidal Placenta: Ex: Rat, Bat, Rabbit. On the entire surface of blastocyst the villi are in the form of discs. When the embryo Is growing It movesaway from uterus hence the with look like a disc. These villi are Intimately connected with uterus. Hence during parturitlon much uterine tissue is damaged.
CLASSIFICATION OF PLACENTA (BASING ON HISTOLOGY):
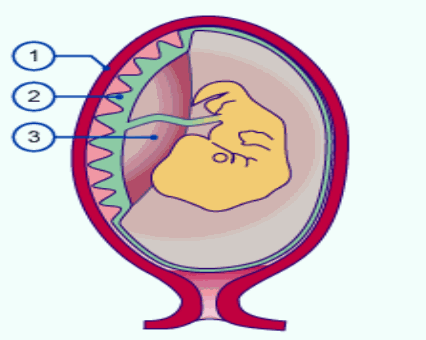
According to number of layers of cells present between foetus and uterus blood supply the placenta Is classified into five types.
a) Epithelio chorlal placenta: Ex: Pig, Horse, (Ungulates Lemmures)
The foetal chorion Is In contact with eplthelium of the uterus hence it is called epithello chorial placenta. In between foetal, maternal parts six layers are present.
- Endothelium of mother blood vessel.
- Maternal syndesmose connective tissue.
- Epitheliurn of mother
- Chorion of foetus.
- Foetus connective tissue (syndesmose
- Endothellum of foetal blood vessel.
If all the six layers are present the placenta is called epithello chorlal placenta.
b) Syndeumose chorial placenta: Ex: Sheep, Cow.
The allanto-chorianic vith will pierce into the uterus of the mother, the chorion will come in contact with syndesmose of mother’s uterus. Hence iti s called syndesmose chorial.
c) Endothelio chorial placenta: Ex: Dog, Carnivores. The chàrion of the foetus will come in contact with the endotheli of mother ‘s uterus, hence it is called endothelio-chorial placenta.
d) Hemochorial placenta: Ex: Bat, Man, Primates, Insectivores.
The placental connections are more lntimate. The chorion of foetus will float In the blood pools of mother’s utiras. Hence It Is called haemochorIal placenta.
e) Hemo endothelial placenta: Ex: Rat, Rabbit, Hence guinea-pig will float In mother’s blood. Hence it called hemo endothelial placenta.

Share this info graphic
<p><strong>Please include attribution to bioscience.pk with this graphic.</strong><br /><br /><a href='https://www.bioscience.pk/topics/zoology/item/732-placenta-in-mammals-structure-types-and-functions'><img src='https://www.bioscience.pk/images/Types.of.Placenta.in.Mammals.jpg' alt='placentainmammals' 540px border='0' /></a></p>
FUNCTIONS OF PLACENTA:
- Placenta will form a physiological barrier between mother and foetus. It will possess foetal and maternal blood mixing.
- Placenta allows the diffusion of monosacharides, amino adds, hormones, vitamins, oxygen, .carbondioxide, water and other waste materials, because of this it supplies food, oxygen to foetus.
- It works as an excretory organ of foetus. It releases the nitrogenous waste materials Into mother blood.
- It works as an endocrine gland. It will secretes lactogen ,progesterone,etc. hormones.
- The placenta will manufacture fructose from glucose.
Tags:
End of the article