PENICILLIN DISC TEST
To test the organism's susceptibility to antibiotic penicillin.
Objective:
To test the organism's susceptibility to antibiotic penicillin.
Discovery of Penicillin
The discovery of penicillin's antibiotic powers is attributed to Alexander Fleming. The story goes that he returned to his laboratory one day in September 1928 to find a Petri dish containing Staphylococcus bacteria with its lid removed.
The dish had become contaminated by blue-green mold. He noted that there was a clear ring surrounding the mold where the bacteria had been inhibited from growing.
This discovery of the mold - Penicillium notatum - and his recognition of its special powers set the wheels in motion to create one of the most used drugs in medical history.
In March 1942, Anne Miller became the first civilian to be treated successfully with penicillin having almost died from a huge infection following a miscarriage.
Although Fleming often gets the accolade for having invented the first antibiotic, there was a lot of work to do before penicillin could become as commonly used and useful as it is today.
The bulk of the work was eventually carried out by scientists who had a much better-stocked laboratory and a deeper understanding of chemistry than Fleming. Dr. Howard Florey, Dr. Norman Heatley, and Dr. Ernst Chain carried out the first in-depth and focused studies.
Interestingly, and with impressive foresight, Fleming's Nobel Prize acceptance speech warned that the overuse of penicillin might, one day, lead to bacterial resistance.
Test Procedure
- Pick a single pure colony with a sterile swab to inoculate a SBA plate. Streak the entire blood agar plate with the swab. Turn plate 90 degrees and re-streak with the same swab. Blood agar plate must be used for optochin testing since all species of Streptococcus are fastidious organisms and require extra enrichment for growth.
- With alcohol flamed forceps, aseptically remove an optochin disc and apply to the center of the plate. Gently apply pressure to disc so that it adheres to the surface of the plate but do not press disc down into the medium.
- Invert plate and incubate for 48 hours at your organism's optimum growth temperature.
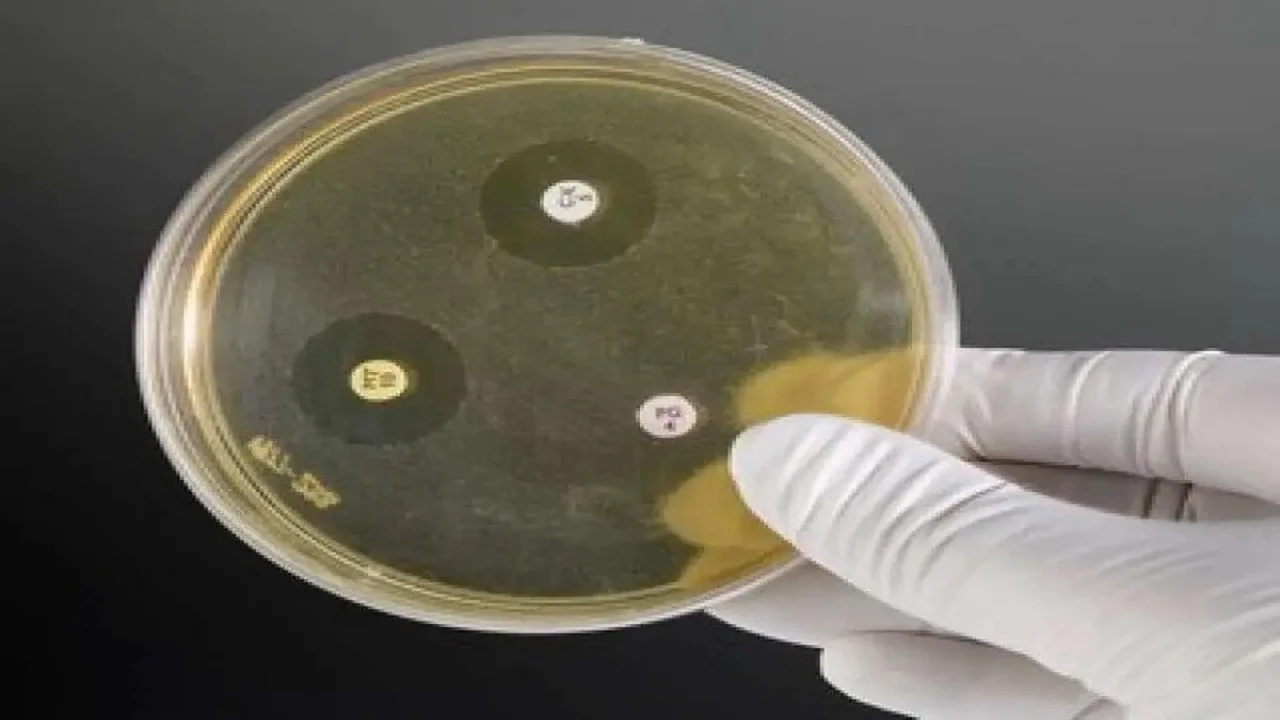
Interpretation
- Sensitive (S): A distinct zone of inhibition (5 to 30 mm) with a clear-cut margin around disc.
- Resistant (R): Growth not inhibited around disc.
Precautions
- Occasionally, a few scattered optochin resistant colonies of S. pneumoniae may be observed in a wide zone of inhibition.
- Occasionally an alpha-Streptococcus spp. may exhibit a very small zone (1 to 2 mm) of inhibition. S. pneumoniae exhibits a zone of inhibition at least 5 mm or greater in diameter.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Comment
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela