A Guide to Gas Chromatography Maintenance and Repair
Mastering Gas Chromatography: A Comprehensive Guide to Precision Analysis, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting Across Industries.
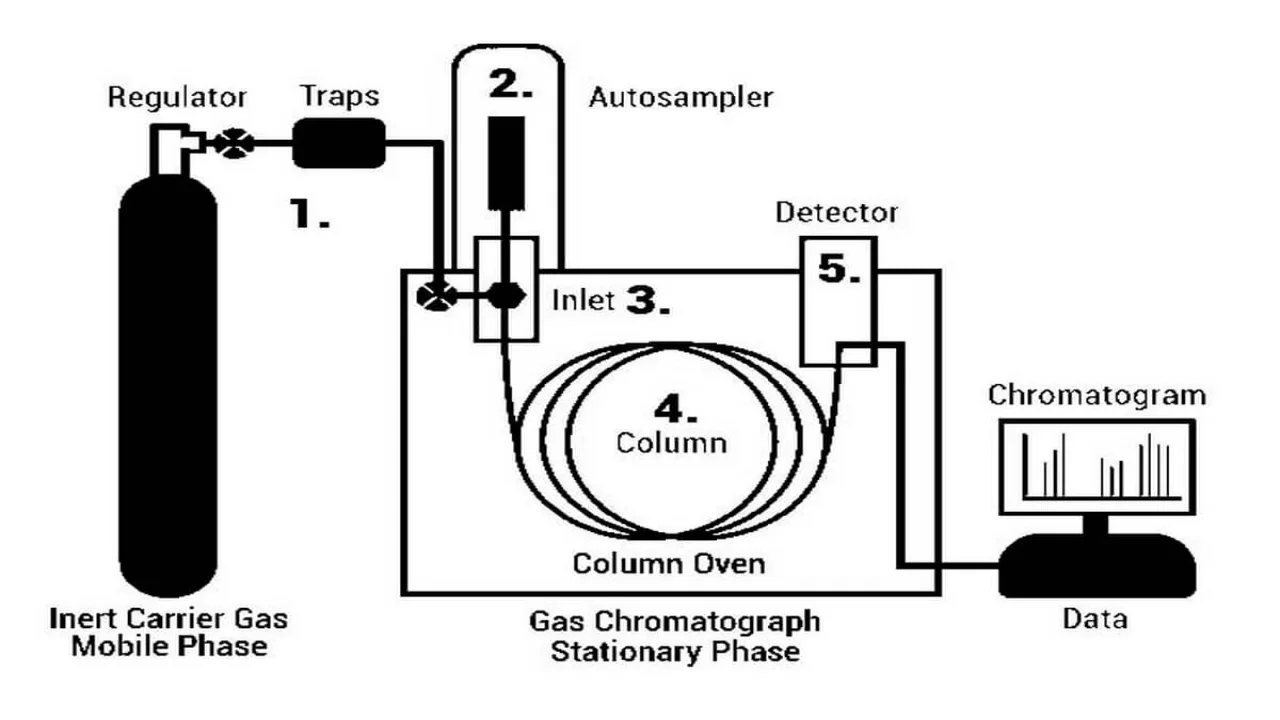
In the intricate world of laboratory instruments, Gas Chromatography (GC) stands as a beacon of analytical precision. Let's unravel the nuances of GC maintenance and repair, exploring its diverse applications and addressing the key factors that contribute to its optimal functionality.
Unleashing the Power of Gas Chromatography:
Gas Chromatography, a cornerstone in analytical chemistry, is renowned for its ability to separate and analyze complex mixtures of gases. Whether in environmental monitoring, food safety testing, or drug development, GC plays a pivotal role in providing accurate and reliable results.
Applications Across Industries:
Environmental Analysis: GC finds its footing in environmental analysis, where it detects and quantifies pollutants in air, water, and soil. This enables scientists to monitor and address environmental challenges proactively.
Pharmaceutical Research: In pharmaceutical research, GC helps analyze drug formulations, ensuring the purity and potency of medications. It's a vital tool in drug development, supporting the creation of safe and effective pharmaceuticals.
Food and Beverage Industry: GC plays a crucial role in the food and beverage industry, helping analyze flavors, fragrances, and contaminants. This ensures the safety and quality of the products we consume.
GC Repair: Navigating Common Issues:
Ensuring the seamless operation of GC instruments involves addressing common issues promptly and efficiently with the help of a GC repair & maintenance solution provider like Peak BioServices that can help with various vendors in the industry.
Column Contamination: Contamination of the GC column can lead to distorted results. Regularly inspect and replace the column as needed to maintain the integrity of the analysis.
Detector Problems: Issues with the detector, whether Flame Ionization Detector (FID) or Mass Spectrometer (MS), can compromise the accuracy of results. Regular maintenance and prompt repair are essential to ensure the detectors function optimally.
Injection Port Blockages: Blockages in the injection port can disrupt the sample introduction process. Regularly clean and inspect the injection port to prevent issues that could affect analysis.
Temperature Fluctuations: Inconsistent temperatures can impact separation efficiency. Regularly calibrate and monitor temperature settings to ensure stable and accurate results.
GC Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and Solving Challenges:
Baseline Drift: If you notice baseline drift, it could indicate issues with the detector or column. Perform routine checks, and if needed, consult with technicians for thorough diagnostics.
Retention Time Shifts: Shifts in retention time may signal issues with column degradation or temperature fluctuations. Address these concerns promptly to maintain the reliability of results.
Poor Peak Shape: Poor peak shapes can arise from column contamination or injector problems. Regularly clean and maintain these components to ensure sharp and well-defined peaks.
GC Maintenance: A Proactive Approach:
Proactive maintenance is the key to the longevity and efficiency of GC instruments.
Regular Column Replacement: Schedule routine column replacements to prevent column deterioration and maintain the quality of separations.
System Calibration: Regularly calibrate the GC system to ensure accurate and reproducible results. This involves checking and adjusting parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates.
Cleanliness is Key: Keep the entire GC system clean, from the injection port to the detector. Regularly clean and inspect these components to prevent contamination and maintain optimal performance.
Mastering the intricacies of GC maintenance and repair is essential for laboratories committed to analytical excellence. By understanding its diverse applications, promptly addressing common issues, and adopting a proactive maintenance approach, scientists and technicians can ensure the seamless operation of Gas Chromatography instruments, contributing to advancements in research and analysis across various industries.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
- Last updated by Dayyal Dungrela, MLT, BSc, BS
Cite this page:
- Comment
- Posted by BS Media