Search
Total 50 results were found for your query Fish.
-
 Zoology
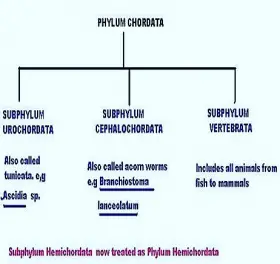
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION PHYLUM CHORDATE
... are marine organisms. Their body is fish-like with notochord and nerve cord persisting throughout life . They extend the entire length of the body. The eyes, and jaws are absent. The fundamental plan of ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
 Zoology
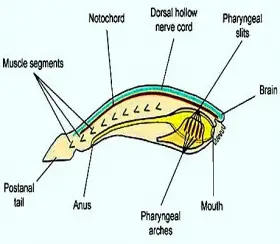
ZoologyBIOLOGY OF CHORDATES
... in this phylum. The vertebrates are fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. All these animals appear to be quite different from each other .However all of them possess certain common characters. ...Created on 04 July 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION OF MAMMALS: THERIA
... Squirrel, Hystrix - Porcupine. 9. Order: Cetecea: Large aquatic animals. Body is spindle shaped and fish like. Hair is absent. Neck is absent. Fore limbs are modified into paddles. ...Created on 01 July 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION OF AVES
... fish eating birds. Four toes are webbed. 5. Order: Clconiformee: Ex: Ardea (great blue heron) Neck is long and Legs are long Web is absent. 6. Order: Ariseriformea: Ex: ...Created on 01 July 2017 -
 Zoology
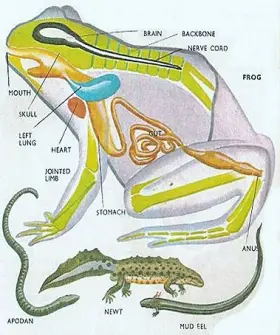
ZoologyGENERAL CHARACTERS OF AMPHIBIA
Amphibians are cold blooded vertebrates. In the Devonian period of palaeozoic era they were originated from fishes, in the carboniferous period, they increased their number, hence that period is called ...Created on 30 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyAN INTRODUCTION TO AMPHIBIANS
Amphibians are the earliest tetrapods. They were descended from fish like ancestors. They were developed in the Devonian period. They flourished during carboniferous period. It is called “Age of Amphibians”. ...Created on 30 June 2017 -
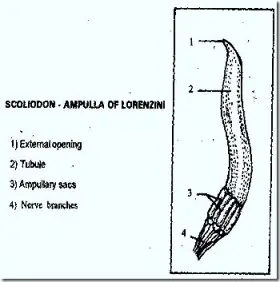 Zoology
ZoologyAMPULIAE OF LORENZINI IN FISHES
On the upper and lower surfaces of the head a number of tin- branched structures are present. They are called ampullae of lorenzini. Each ampulla contains two parts. Expanded ampullary sac and ...Created on 30 June 2017 -
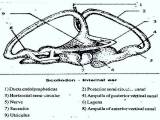 Zoology
ZoologyINTERNAL EAR OF SHARK (OR) MEMBRANOUS LABRYTH
It lies in the auditory capsule of the skull. It is useful for maintenance of equilibrium. In the fish external and middle ears are absent. Internal eats covered by cartilaginous labyrinth. A space is ...Created on 30 June 2017 -
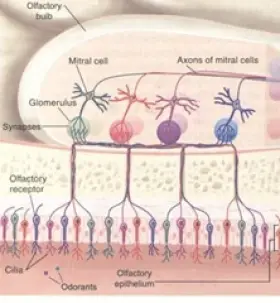 Zoology
ZoologyOLFACTORY LOBES IN SHARKS
In Scoliodon the olfactory lobes are olfactory organs or nasal sacs. They are present in the olfactory sacs of cranium. They develop from the ectoderm. They open out through the exterior by external ...Created on 30 June 2017 -
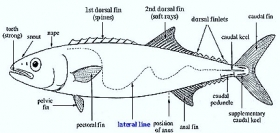 Zoology
ZoologyNEUROMAST SYSTEM OR LATERAL TINS SENSE ORGANS IN FISHES
On the lateral sides of think and tall lateral line canals are present. They are present deeply In the dermis. In the head region there are connected by transverse canals. In the head region cephalic canals ...Created on 30 June 2017