Fasciola Hepatica (Sheep Liver Fluke) Morphology and Physiology
Fasciola hepatica is an endoparasite of sheep. In 1879 "B.C. Jeham de Brie" reported Fasciola from the liver of sheep. Thomas and Leuokart" experimentally demonstrated the changes of liver fluke in a pond snail. It belongs to
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Class: Trematoda
- Order: Digenea
It is distributed throughout the world. It attacks sheep and causes liver rot disease in them.
External morphology
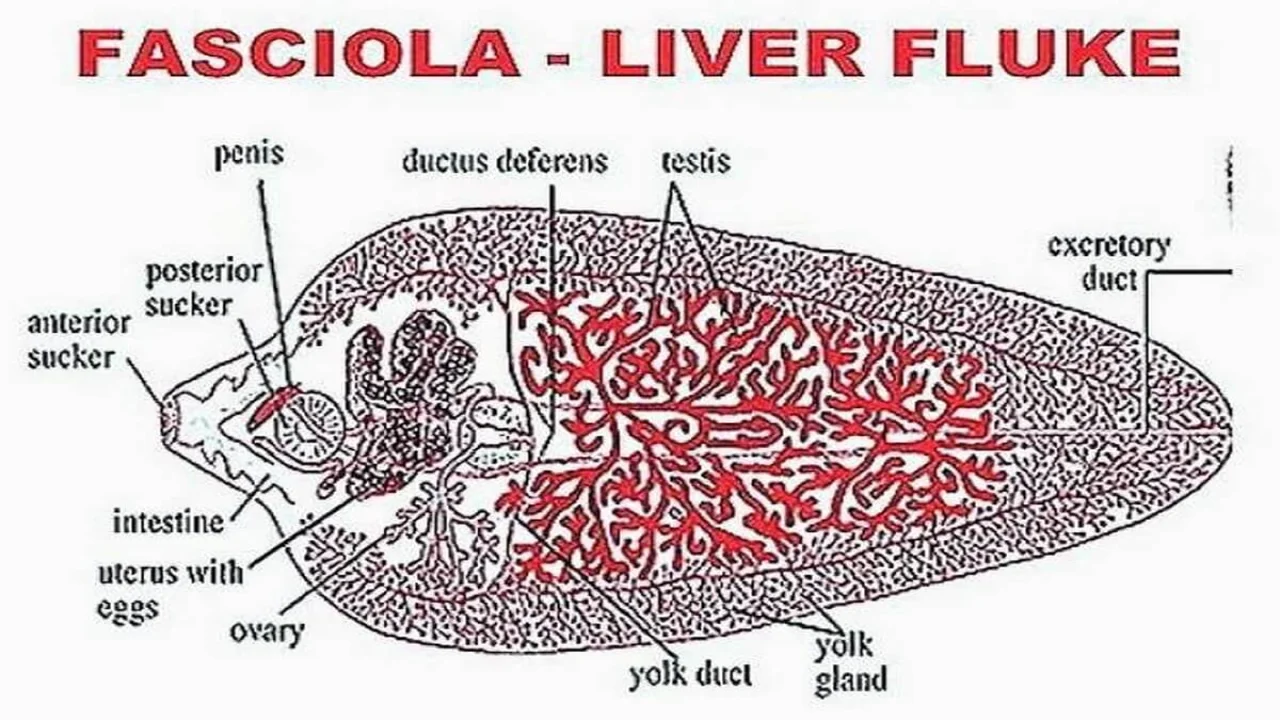
- General morphology: Its body is oval, dorsoventrally flat, and looks like a leaf. Its body is soft. It is 1.5 to 5 cm in length; 5 to 1.5 cm in width in the middle of the body. The body is pink in color. The digestive system is brown because of the presence of ingested bile.
- External openings:
- At the anterior end mouth opening is present.
- On the ventral side above the ventral sucker a small genital opening is present.
- In the breeding season on the dorsal side a small opening of Laurer's canal is developed.
- At the posterior end a small excretory opening is present.
- Suckers: Two suckers are present.
- At the anterior around the mouth an oral sucker is present. It is 1 mm. in diameter It is useful for ingestion and adhesion and also
- On the ventral side a ventral sucker is present 3 to 4 mm. away from the anterior end. It is a large sucker. It is useful for adhesion.
- T.S. of Body Wall: The body wall of Fasciola shows the following parts.
- Tegument: It is an outer cytoplasmic layer. It shows microvilli. It is a syncytial layer. It is thick. It contains mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. It contains scleroprotein and is resistant to digestive juices. It shows backwardly directed spines.
- Basement membrane: Below the tegument basement membrane is present.
- Musculature: Below the basement membrane muscle layers are seen. The muscles are circular and longitudinal. Below the longitudinal muscles, oblique muscles are also present.
- Below the muscles loose parenchymatous tissue is present. In this tissue, various organs are enclosed. In this tissue, big mesenchyme cells are present. In this parenchyma, all systems are included like the digestive, excretory, and nervous systems.
- Digestive system: The digestive system is well developed. As the circulatory system is absent, it distributes digested food to all parts of the body. It shows only the mouth. Anus is absent. At the anterior end of the body, a mouth opening is present. It is surrounded by an oral sucker. The mouth leads into the buccal cavity, which leads into the pharynx. It is a thick chamber with glands. It leads into a narrow esophagus. It opens into the intestine. This intestine is divided into branches. Each branch gives several irregular side branches. The two branches will end blindly near the posterior end of the animal. The intestine is lined by the endoderm. These animals suck the tissue, fluid, lymph, and bile from the host. The process of digestion is not known. The digested food is distributed to all body parts of the branches of the intestine. The tegument absorbs glucose from the host directly.
- Excretory system: In a liver fluke, the excretion is carried on by flame cells. The liver fluke shows a big median longitudinal excretory canal. From it, several branches will arise. They branch again. The fine branches end with flame cells. These cells are buried in the mesenchyme. The median longitudinal excretory canal opens at the posterior end through an excretory opening.
- Flame cells: In a liver fluke, the excretion is carried on by flame cells. These flame cells are distributed in the mesenchyme. Each cell is irregular in shape. It is covered by a thin wall. It produces branches that look like pseudopodia. The lumen of the cell is big and the nucleus is pushed to one side. In the lumen a group of flagella are present. They show movement. It looks like the flickering of a flame hence it is called a flame cell. From the mesenchyme, the flame cells absorb the nitrogenous wastes and amino acids. These wastes are pushed into the capillaries to which flame cells are connected. From there wastes enter into the median longitudinal excretory canal and are finally sent out through the excretory pore.
Respiration
Fasciola hepatica lives in the bile duct of sheep as an endoparasite. In this environment, O2 supply is very limited. Hence it takes up anaerobic respiration. The CO2 formed will be sent out through the body surface by diffusion.
Nervous system
The nervous system is well developed in Fasciola. Sense organs are not developed except, tangoreceptors of suckers.
Nerve ring
On the dorsal lateral sides of the esophagus, two cerebral ganglia and a ventral ganglion are present. They are all united and a nerve ring is formed around the oesophagus.
Longitudinal nerve cords
From the nerve ring, 3 pairs of longitudinal nerve cords will arise. They are
- 1 pair on the dorsal side
- 1 pair on the ventral side and
- 1 pair on lateral sides
The lateral longitudinal nerve cords are very long and well-developed. They show transverse connectives.
From the nerve ring and all longitudinal nerve cords, fine nerves will go to all parts of the body.
Reproductive system
Fasciola is a bisexual animal. It shows both male and female reproductive organs.
- Male reproductive system: The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testis lying one above the other in the body. Each testis is highly branched. From each testis were deferens arises. The two sperm ducts go forward and unite. The seminal vesicle is continued as an ejaculatory duct. It opens into the genital atrium which lies above the ventral sucker. The terminal part of the ejaculatory duct is highly muscular and known as the penis or cirrus. When not in use the cirrus is present in a sac called the cirrus sac.
- Female reproductive system: The female reproductive system consists of a single highly branched ovary lying on the right side of the body. From the ovary oviduct arises which proceeds towards the center of the body. On each side of the body, two longitudinal vitelline ducts are present. Several vitelline glands are present. They unite with longitudinal vitelline ducts through small ducts. The longitudinal ducts are connected by a transverse vitelline duct which is positioned a bit above the middle line of the body. From this transverse vitelline duct is positioned a bit above the middle line of the body. From this transverse vitelline duct, a yolk reservoir arises. This gives a median vitelline duct and it unites with the oviduct. The combined duct opens into an ootype. At the junction of the vitelline duct and oviduct, a uterus arises. It is a long coiled tube. It opens into the genital atrium through the female genital opening. At the junction of the uterus, oviduct, and vitelline duct, Mehlis glands are present. The junction of the three ducts is called Ootype.
During breeding season from this junction, a temporary canal arises called Laurer's canal. It opens on the dorsal side of the body.
The information on this page is peer reviewed by a qualified editorial review board member. Learn more about us and our editorial process.
Last reviewed on .
Article history
- Latest version
Cite this page:
- Comment
- Posted by Dayyal Dungrela