Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Zoology
CRANIAL NERVES IN RABBIT
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Monday, 29 May 2017 16:58 UTC
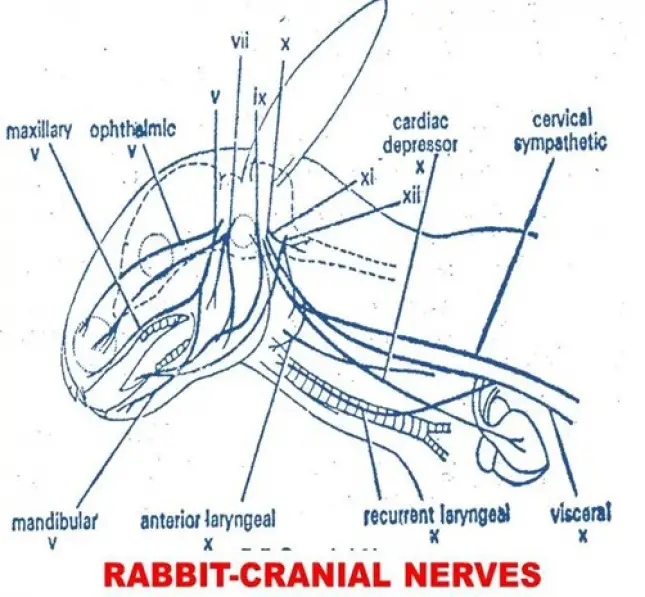
In Rabbit there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
I. OLFACTORY NERVE:
This is a sensory nerve arising from the anterior end of the olfactory lobe and innervates neurosensory cells of olfactory chamber. Olfactory impulses are conducted to the brain from nasal sac through this nerve.
II. OPTIC NERVE:
It is a sensory nerve arising from the lateral side of the optic lobe. The nerve innervates retina of the eye. Visual impulses are carried to the brain from retina through this nerve. These nerves form optic chiasma on the ventral surface of the brain.
III. OCCULOMOTOR NERVE:
This is a motor nerve arising from crura cerebri of mid brain. It innervates the internal, superior rectus, inferior rectus, anterior rectus and inferior oblique muscles of eye ball.
IV. TROCHLEAR OR PATHETIC NERVE:
Trochlear nerve is a small motor nerve arising from the dorsal side of the brain between optic lobes and cerebellum. This nerve innervates the superior oblique muscle of eye ball.
V. TRIGEMINAL NERVE:
This is a mixed nerve arising from anterolateral parts of medulla oblongata. At its base, it bears a ganglion called gasserian ganglion. It divides into 3 branches.
A. Opthalmic Nerve: It passes along the dorsal border of the orbit (between the skull and the eye ball) and innervates the skin of snout. It is sensory in nature.
B. Maxilary Nerve: It runs below the eye ball and supplies to the skin of upper jaw. It is also sensory in nature,
C. Mandibular Nerve: It runs along the outerside of the lower jaw and innervates muscles and skin. It is mixed in nature.
VI. ABDUCENS NERVE:
It is a small motor nerve arising from the ventral side of medulla oblongata and innervates the external rectus and retractor bulbi muscles of eye ball.
VII. FACIAL NERVE
It is a mixed nerve arising from lateral sides of the medulla oblongata just behind the 5th cranial nerve. It joins with gasserian ganglion before leaving the skull. It is divided into two branches.
A. Palatine Nerve: It runs forward below the orbit and innervates mucous membrane (roof) of the buccal cavity. It is sensory in nature.
B. Hyomandibualar Nerve: It crosses over columellauris of the middle ear and innervates the muscles of the lower jaw and hyoid apparatus . It is motor in nature.
VIII. AUDITORY OR ACOUSTIC NERVE:
This is a sensory nerve arising from the lateral sides of medulla and innervates the sensory cells of internal ear.
IX. GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE:
This is a mixed nerve arising from the lateral sides of medulla behind auditory nerve. It innervates mucous membrane of the tongue, pharynx and muscles of hyoid. It gives out a delicate branch which joins hyomandibular branch of the seventh cranial nerve.
X. VAGUS OR PNEUMOGASTRIC NERVE:
This is the largest mixed nerve arising from the lateral sides of the medulla oblongata. It has common origin with the ninth nerve. After emerging from skull, the nerve swells and forms a vagus ganglion. The vagus nerve is divide into five branches.
A. Cutaneous Nerve: it is a sensory nerve innervating the dorsal body wall
B. Cardiac Nerve: It is a motor nerve innervating the heart.
C. Laryngeal Nerve: It is a mixed nerve going to the laryngo-tracheal chamber.
D. Pulmonary Nerve: It is a motor nerve going to the lungs.
E. Gastric Nerve: It is a mixed nerve innervating the stomach.
XI. SPINAL ACCESSORY:
it arises from medulla. It is motor in function. Spinal accessory is innervated in the muscles of shoulder and neck.
XII. HYPOGLOSSAL:
it arises from the ventro posterior end of medulla. It is motor in function. Hypoglossal is in nervated in the muscles of tongue.
|
CRANIAL NERVES |
||
|
Sensory nerves |
Motor nerves |
Mixed nerves |
|
Olfactory (1st) |
Occulomotor (3rd) |
Trigeminal (5th) |
|
Optic (2nd) |
Trochlear (4th) |
Facial (7th) |
|
Auditory (8th) |
Abducens (6th) |
Glassopharyngeal (9th) |
|
Spinal accessory (11th) |
Vagus nerve (10th) |
|
|
Hypoglossal (12th) |
||
End of the article