Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Zoology
ARTERIAL SYSTEM OF RABBIT
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Monday, 22 May 2017 16:59 UTC
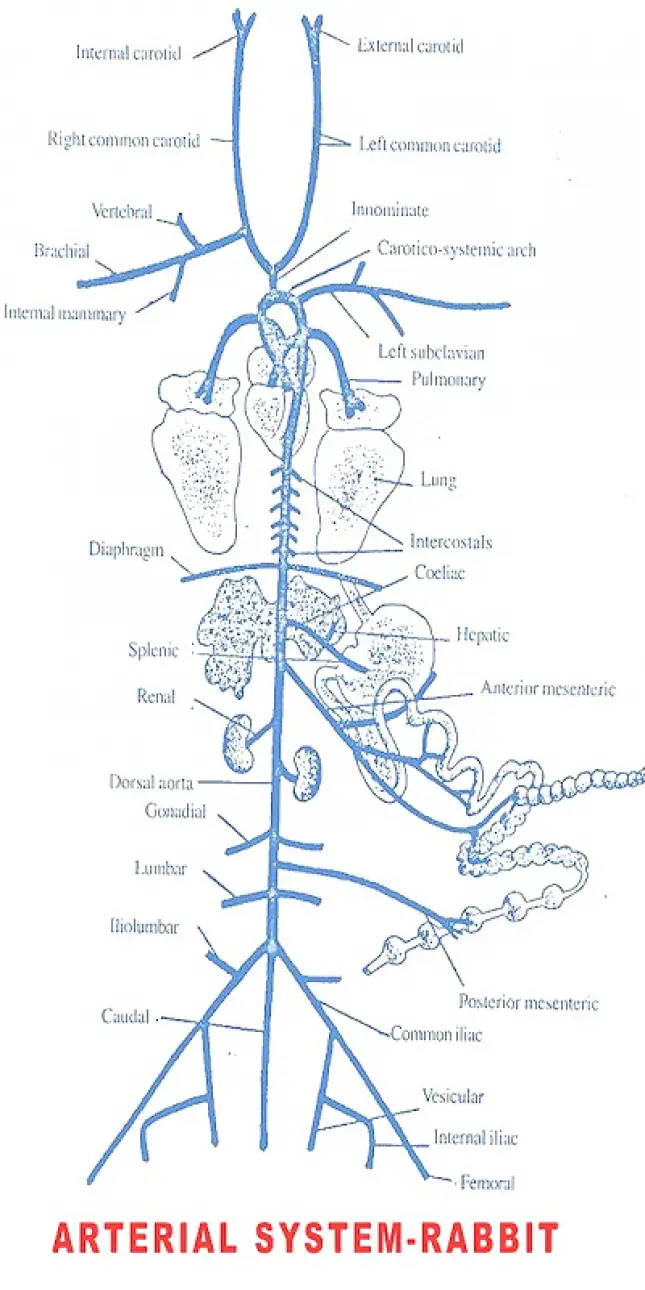
The circulation concerned with supply of blood to different organs is called arterial system.The heart of rabbit supplies blood to different organs of the body by means of two important aortic trunks namely
I. Carotico - systemic trunk and
II. Pulmonary trunk.
- The carotico - systemic trunk originates from left ventricle and bends towards left side.
- Two coronary arteries, a right and left originate from the systemic trunk immediately soon after its emergence from the ventricle.
- The coronary arteries supply blood to the wall of the heart.
- A left sub-clavian artery originates from the left side of carotico-systemic trunk at its bend.
- An innominate artery also arises from carotico - systemic trunk. The innominate artery gives three branches namely
I. Right sub-clavian
II. Right carotid and
III. Left carotid.
Each carotid artery is divided into two branches namely
a. External carotid artery - that supplies blood to tongue, jaw-muscles and salivary glands.
b. Internal carotid artery - It supplies blood to cranium and parts of the brain.
- Each sub-clavian also gives three arteries namely
a. Brachial artery - supplying blood to the forelimbs.
b. Vertebral artery - supplying blood to the cavities of cervical vertebrae, spinal cord and parts of the brain.
c. Internal mammary artery: It supplies blood to ventral side of thoracic muscles. Then it terminates as superior epigastric artery to supply blood to ventral muscles.
- The carotico systemic aorta then bends to the left side and runs below vertebral column as dorsal aorta.
- In thoracic region dorsal aorta gives off a series of small paired intercostal arteries supplying blood to the body wall.
- A pair of small phrenic arteries also arise one on either side and supply blood to the diaphragm.
- Then the dorsal aorta passes into abdominal cavity through the diaphragm.
- In the abdominal cavity the aorta gives a coeliac artery supplying blood to liver, spleen, stomach and duodenum. An anterior mesenteric artery also originates from the dorsal aorta below the coeliac artery.
- The anterior mesenteric artery divides into number of branches supplying to small intestine, pancreas, caecum and colon.
- The dorsal aorta supplies blood to kidneys by means of a pair renal arteries.
- Right renal artery is slightly anterior to left renal artery.
- A pair of gonadial arteries also arise from the dorsal aorta to supply blood to gonads.
- In male rabbit they are called spermatic arteries supplying blood to the epididymis, vasdeferens and testes.
- In female rabbit they are called ovarian arteries supplying blood to ovaries.
- The dorsal aorta also gives a posterior mesenteric artery that supplies blood to hinder part of the rectum and lower part of colon.
- A pair of lumbar arteries arise from the dorsal aorta to supply to the dorsal body wall.
- The dorsal aorta then divides into two common iliac arteries and a median caudal artery to the tail.
- Each common iliac artery gives a small ilio-lumbar artery that supplies to dorsal body wall.
The common iliac artery divides into
I. Internal iliac or hypogastric artery which supplies to the organs of the pelvis and
II. External iliac artery that supplies to the hind limb.
- A small vesicular artery also arises from the common iliac that supplies to urinary bladder and also the uterus in female.
- The external iliac terminates as femoral artery in each hind limb.
- The pulmonary aorta originates from the base of the right ventricle.
- It divides into two pulmonary arteries supplying blood to the lungs.
- The pulmonary arteries carry impure or deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle into the lungs for oxygenation.
End of the article