Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Zoology
STRUCTURE OF SHARK EYES
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Thursday, 04 January 2018 15:37 UTC
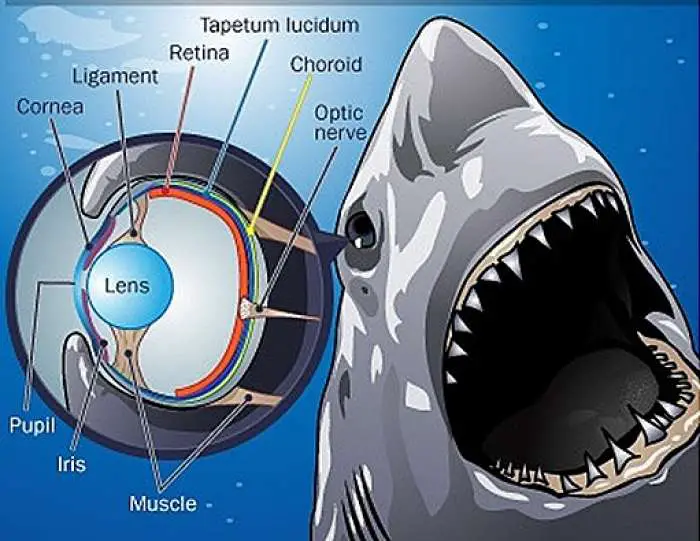
SHARK EYE (SCOLIODON EYE) – ANATOMY
Shark two eyes are present on the head. They are located in the orbits and are laterally directed.
The eye is large in size and elliptical body. It is a hollow structure. It is covered by three coats.
1) The fibrous outer coat is thick. It protects the eyeball and maintains its form. It has large posterior scierotic and anterior transparent cornea The sclerotic coat is cartilagenous.lt is hidden in the orbit. A small portion is visible externally, called the white of the eye. The cornea is composed of connective tissue. It is covered by a transparent epithelium called conjunctiva. The cornea permits the light to pass into the eye.
2) The middle coat has three distinct regions.
a) The choroidis composed of a soft connective tissue with pigment cells and blood vessels
b) The choroid is adjacent to the retina and contain light reflecting crystals called tapetum lucidium.
c) At the junction of the sclerotic and the cornea the middle coat, abruptly bends into the cavity of the eye as "iris", it has slit called pupil. Behind the periphery of the iris, the middle coat is thicker, and less pigmented and is called the ciliary body. It has no muscles and plays no role in accommodation.
3) The retina is very delicate and lines the whole of the middle coat, it has three regions.
a) optic part is in contact with the choroid. It is sensitive to light,
b) The ciliary and
c) Iridial parts are non sensory parts.
The point of the retina from where the optic nerve leaves the eye is called the blind spot. This region has no receptors. It is not sensitive the light. The retina contains rods. The cones are absent. The fish is colour blind. Its eye is adapted to "dim light" vision.
A solid transparent crystalline lens, lies just behind the pupil. It is held in place by a gelatinous suspensory ligament. It extends from the lens capsule to the ciliary processes. The lens divides the cavity of the eye into two chambers. The anterior smaller aqueous chamber and the posterior larger vitreous chamber. The aqueous chamber is partly divided into anterior and posterior parts by iris. It has aqueous humour. The vitreous chamber is filled with the vitreous humour. The humours keep the eye inflated and aid in focusing Sight rays on the retina of shark.
The eye is protected by three lids. The upper end lower lids are folds of skin are immovable. The third eyelid, the nictineting membrane is well developed. It covers the eye fully. It is a growth of the anterior region of the lower eyelid. Lacrimal gland is absent.
Tags:
End of the article