Medically reviewed and approved by a board-certified member
Hemotology
BLOOD CLOTTING PROCESS
By BS MediaTwitter Profile | Updated: Saturday, 09 February 2019 21:14 UTC
COAGULATION OF BLOOD MECHANISM
The blood remains in a fluid state as long as it is inside the blood vessels. But when it comes in contact with external atmospheric conditions, it changes into a jelly-like mass. The blood is then said to be clotted or coagulated.
When a blood clot is observed under the microscope, it consists of a network like structure in which the blood cells are entangled. A light Yellow fluid comes out from the clot and is called serum. Different theories were put forward to explain the mechanism of blood coagulation. They are a. BEST AND TAYLOR'S THEORY, b. HOWELL'S THEORY and c. FULD AND SPIRO'S THEORY
1. BEST AND TAYLOR'S THEORY
- According to Best and Taylor, four substances are necessary for blood clotting.
- They are prothrombin, calcium, Thromboplastin, and fibrinogen. Prothrombin is produced by the liver and is also present in small quantities in the plasma of blood. K Vitamin helps in the synthesis of prothrombin in the liver.
- Calcium ions are present in the plasma as inorganic constituents.
- Fibrinogen is a soluble protein found dissolved in the plasma.
- When an injury is formed, thromboplastin is liberated from the injured tissue.
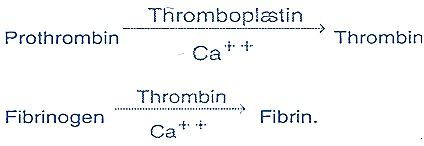
- The released thromboplastin acts on prothrombin in presence of calcium ions and converts it into active thrombin.
- The thrombin in its turn acts upon fibrinogen, converting it into fibrin.
- The blood cells are entangled within fibrin thread to form a clot.
- The blood within the blood vessels never clots.
- If clotting occurs in the blood vessels it is called thrombosis and the clot is known as a thrombus.
- However, the blood clotting in blood vessels is prevented by antithrombin that is heparin.
- Heparin is also produced from the liver and present in the blood.
2. HOWELL’S THEORY
- According to Howell, the prothrombin is supposed to be converted into thrombin by the action of calcium alone.
- Antithrombin prevents the activation of prothrombin within blood vessels.
- When the blood vessels are injured, the tissue cells produce a substance known as cephalin protein.
- This neutralizes antithrombin and thus permits the calcium to react with prothrombin.
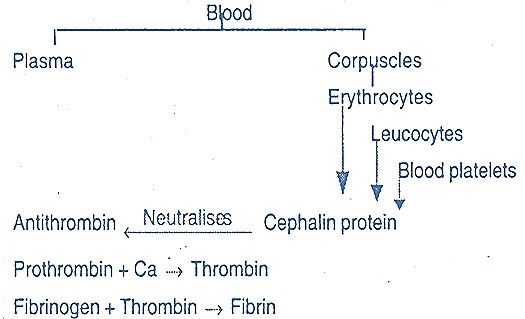
- As a result, thrombin is formed. Thrombin reacts with fibrinogen to form fibrin.
3. FULD AND SPIRO'S THEORY
- According to this theory, an enzyme called thrombokinase plays an important role in blood coagulation. Thrombokinase is nothing but thromboplastin secreted from ruptured blood platelets.
- Thromboplastin converts prothrombin into thrombin which in turn changes fibrinogen into fibrin.
Thrombokinase
Prothrombin ----------------------------->Thrombin
Ca++
Ca++
Fibrinogen + Thrombin ------------> Fibrin
- In all the above methods of coagulation, the soluble fibrinogen is converted into insoluble fibrin to form a clot.
- This clot is also known as Buffy coat.
- The blood fails to coagulate in some people even when a wound appears on the body.
- This condition is called Haemophilia which is hereditary.
- Sometimes it is most fatal. Haemophilia is also called Royal disease since it is most common in the Royal family of British.
Tags:
End of the article