Search
Total 23 results were found for your query MOLLUSCA.
-
 Zoology
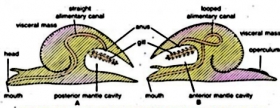
ZoologyTORSION AND DETORSION IN MOLLUSCA
TORSION Torsion is a process in which the viscero-pallium rotates anti-clockwise through 180° from its initial position during larval development. So that the mantle cavity, with its pallial complex, ...Created on 11 February 2018 -
 Zoology
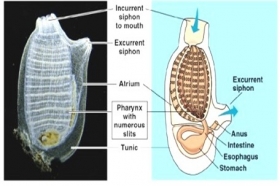
ZoologyGENERAL CHARACTERS OF UROCHORDATA
The tunicates were first regarded as sponges. Lamark in 1816 placed Tunicata in between the Radiata and Vermes in his system of classification. Later, they were included in Mollusca. In 1866 Kowalevsky ...Created on 06 July 2017 -
 Zoology
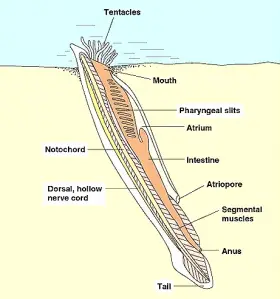
ZoologyEXTERNAL CHARACTERS OF AMPHIOXUS
Amphioxus belongs to Cephalochordate. In 1778 Amphioxus was first discovered and described by Palias. He called it a Molluscan animal. In 1834, it was described as a chordate animal by Costa. He called ...Created on 05 July 2017 -
 Zoology
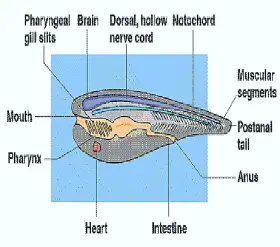
ZoologyCLASSIFICATION AND SYSTEMIC POSITION OF CEPHALOCHORDATE
... includes Amphioxus or Branchiostoma. Pallas described this animal first. He named it as Umax lancealatus, He included this in Mollusca. In 1834, costa described its chordata features. In 1836, ...Created on 05 July 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyLARVAES OF ANIMALS
... Glaucothoea is larvae of Hermit Crab Alima is larvae of Squilla Mysis is larvae of Prawn Schizopod is larvae of Lobsters Nauplius is larvae of Crustacean MOLLUSCA LARVAE Glochidium ...Created on 22 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyBIOLOGY TERMS: FIRST USERS AND COINERS
... TAXONOMY TERMS FIRST USED AND FIRST COINED Virus Beijerink Protozoa Gold Fuss Porifera Robert Grant Parazoa Solas Coelenterata Leukart Mollusca Johnston Annelida Lamarck ...Created on 15 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyFRESH WATER FISHES IN AQUACULTURE
... The head is flat with laterally compressed body. It possesses accessory respiratory organs and lives in lake kolleru of A.P. It feeds on molluscans, algae and grows to a size of 45 cm. 3. Clarias ...Created on 13 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyAQUA CULTURE (PISCI CULTURE)
... fin fish fishery. The fishery concerned with fishes having shell is called shell fish fishery. Molluscans, Crustaceans such as crabs, lobsters and prawns constitute shell fish fishery. The ...Created on 13 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyZOOGEOGRAPHY: AUSTRALIAN REGION
The entire earth shows animal fauna. As per the distribution of the fauna the earth is divided into Zoogeographical regions. Australian region contains Australia, Newzealand, New Guinea and nearby ...Created on 12 June 2017 -
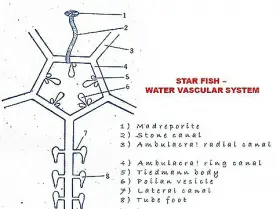 Zoology
ZoologyWATER VASCULAR SYSTEM IN STARFISH
In Echinoderms a peculiar system is met with. It is filled with sea water, it is called water vascular system or Ambulacral system. The entire system is lined with ciliated epithelium. This system is well ...Created on 05 June 2017 -
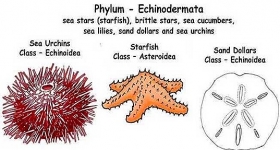 Zoology
ZoologyINTRODUCTION TO PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA
Jacob Klein (1734) first used the term Echinodermata for sea urchins. Linnaeus in 1758 placed Asterias, Echinus and Holothuria under Mollusca. Lamarck (1801) included these animals in the order Echinoderm ...Created on 05 June 2017 -
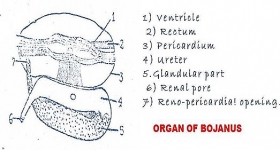 Zoology
ZoologyEXCRETORY SYSTEM IN UNIO
The excretory system of Unio includes a pair of kidneys (organs of Bojanus) a pericardial gland (Keber's organ). The kidneys include the coelomic cavities. Organ of Bojanus: These are present below ...Created on 05 June 2017 -
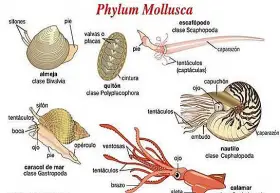 Zoology
ZoologyCHARACTERS AND CLASSIFICATION OF PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
GENERAL CHARACTERS & CLASSIFICATION OF MOLLUSCA Introduction: Mollusca includes soft bodied animals. It was first applied by Ariistotle to the cuttle-fish of the Aegean Se. The Moiluscans are soft ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
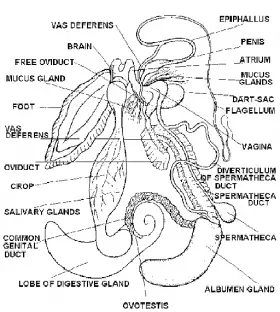 Zoology
ZoologyREPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM IN PILA (SNAIL)
Pila is a unisexual animal. Males and females are separate. Male is smaller than female. Male will show penis at the end of vas deferens. Male Reproductive System It shows testis, vas deferens ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
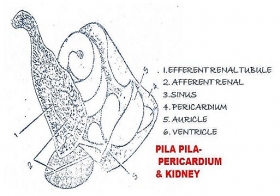 Zoology
ZoologyEXCRETORY SYSTEM IN PILA (SNAIL)
In pila a big kidney will work as an excretory organ. It is called organ of Bojanus. It is present on the left side. It opens to the exterior. It has two chambers. One is on the right anterior side ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
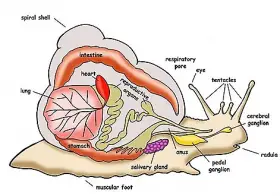 Zoology
ZoologyBLOOD VASCULAR SYSTEM IN PILA (SNAIL)
The blood vascular system cf Pila includes sinuses and blood vessels. This system contains Blood Heart, Pericardium Arteries Veins Sinuses 1. Blood It is liquid tissue. It contains ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologySENSE ORGANS IN PILA (SNAIL)
Pila is an amphibian. It shows many sense organs. They are ospharadium, eyes, statocyst and tentacles 1. Ospharadium Near the left pseudepipodium attached to the pulmonary sac a leaf like ospharadium ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
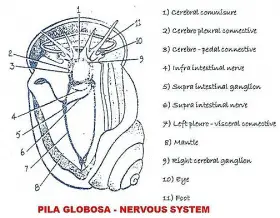 Zoology
ZoologyNERVOUS SYSTEM OF PILA (SNAIL)
Pila shows a well-developed nervous system. This nervous system will show 5 pairs of ganglia, the connectives and commisures and nerves. 1. NERVE GANGLIC Cerebral ganglia Pedal ganglia ...Created on 04 June 2017 -
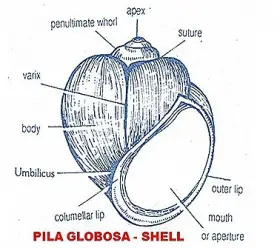 Zoology
ZoologySTRUCTURE, PALLIAL COMPLEX AND INTERNAL SOFT PARTS OF PILA GLOBOSA (APPLE SNAIL)
Pila lives in fresh water ponds, rice fields etc. It is an amphibious form. It belongs to Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda Sub-class: Prosobranchiata Order: Mesogastropoda. SHELL ...Created on 03 June 2017 -
 Zoology
ZoologyPHYLUM MOLLUSCA
"Aristotle" recognised many Cephalopods and Gastropods. In 1650 "Johnson" coined the word "Mollusca". "Linnaeus" included "Mollusca" in the phylum "Verms". In 1790 Cuvier laid the foundation for modern ...Created on 02 June 2017